Figure 1.
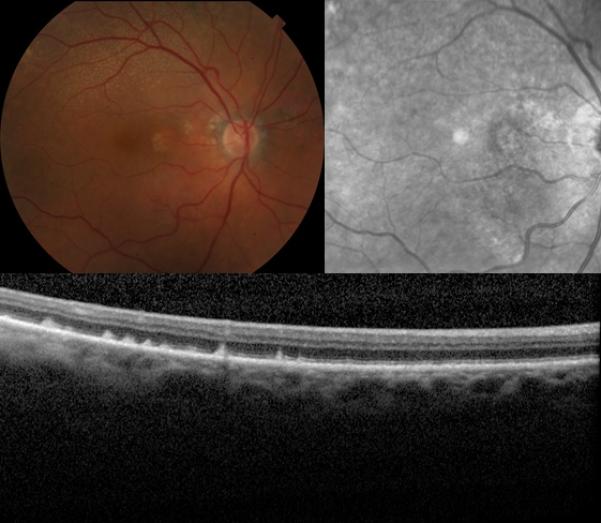
Retinal fundus photographs of the right eye of an 89-year-old female with the reticular pseudodrusen phenotype of age-related macular degeneration. The color photograph (top left) demonstrates the classic presentation of reticular pseudodrusen, identified as yellow or light interlacing networks. Also pictured are the corresponding near-infrared scanning laser ophthalmoscope image of the same eye (top right), showing reticular pseudodrusen as groups of hyporeflectant lesions against a mildly hyperreflectant background in a well-defined pattern, and the optical coherence tomography scan (bottom) of the same eye, showing reticular pseudodrusen as subretinal drusenoid deposits.
