Abstract
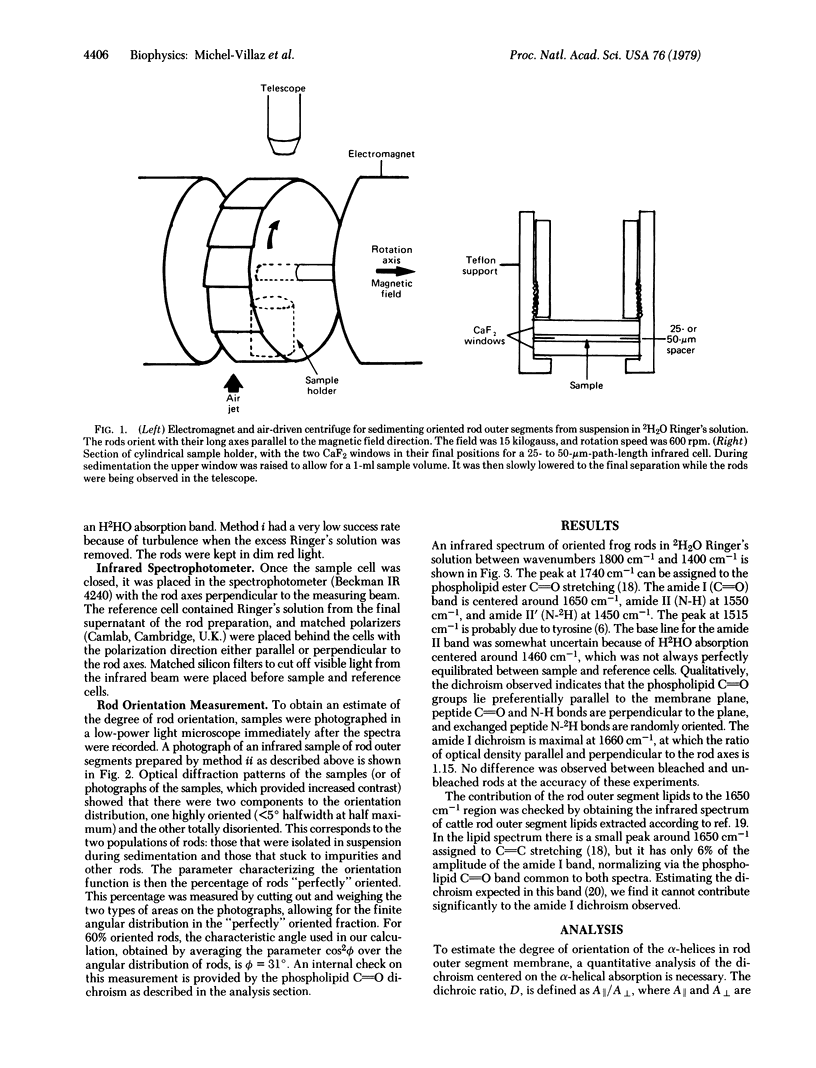
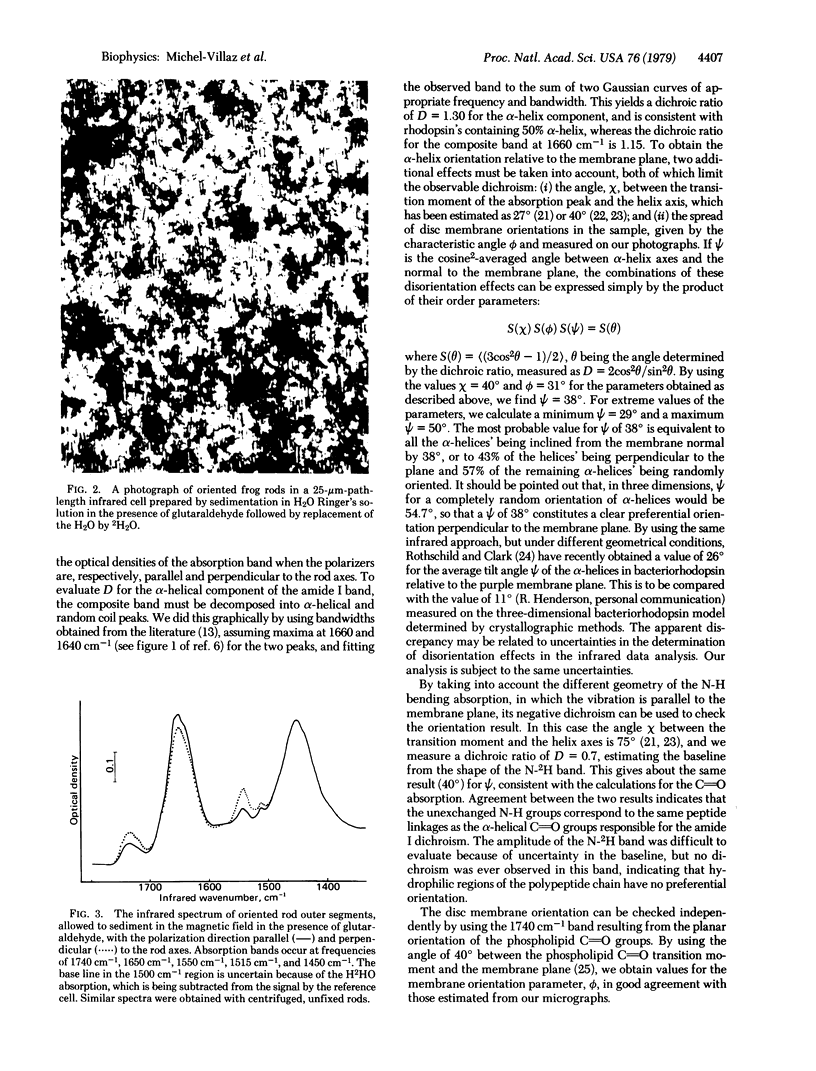
Frog retinal rod outer segments, oriented by a magentic field, were shown to contain rhodopsin alpha-helical segments preferentially aligned perpendicular to the plane of the disc membrane, by the technique of infrared linear dichroism. Infrared absorption parallel and perpendicular to the rod axes by peptide C parallel to O groups, whose absorption band contains alpha-helical and random coil components at slightly different frequencies, showed positive dichroism centered on the alpha-helix frequence. We conclude that the alpha-helical portion of the protein has an average orientation in the transmembrane direction. Furthermore, infrared spectra of rods in 2H2O Ringer's solution exhibit two distinct peptide amino group absorption bands: the unexchanged N-2H band, which is nondichroic. This implies that the oriented part of the protein is in the lipid bilayer, supporting a model for rhodopsin with a hydrophobic core containing partially oriented alpha-helices and hydrophilic ends consisting of unoriented polypeptide.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albert A. D., Litman B. J. Independent structural domains in the membrane protein bovine rhodopsin. Biochemistry. 1978 Sep 19;17(19):3893–3900. doi: 10.1021/bi00612a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRADBURY E. M., BROWN L., DOWNIE A. R., ELLIOTT A., FRASER R. D., HANBY W. E. The structure of the omegaform of poly-Beta-benzyl-L-aspartate. J Mol Biol. 1962 Aug;5:230–247. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80086-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabre M. Diamagnetic anisotropy and orientation of alpha helix in frog rhodopsin and meta II intermediate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5471–5474. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalazonitis N., Chagneux R., Arvanitaki A. Rotation des segments externes des photorécepeurs dans le champ magnétique constant. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1970 Jul 6;271(1):130–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWSON R. M., HEMINGTON N., LINDSAY D. B. The phospholipids of the erythrocyte 'ghosts' of various species. Biochem J. 1960 Nov;77:226–230. doi: 10.1042/bj0770226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fringeli U. P. The structure of lipids and proteins studied by attenuated total reflection (ATR) infrared spectroscopy. II. Oriented layers of a homologous series: phosphatidylethanolamine to phosphatidylcholine. Z Naturforsch C. 1977 Jan-Feb;32(1-2):20–45. doi: 10.1515/znc-1977-1-205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung B. K., Hubbell W. L. Organization of rhodopsin in photoreceptor membranes. 2. Transmembrane organization of bovine rhodopsin: evidence from proteolysis and lactoperoxidase-catalyzed iodination of native and reconstituted membranes. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 17;17(21):4403–4410. doi: 10.1021/bi00614a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R. The structure of the purple membrane from Halobacterium hallobium: analysis of the X-ray diffraction pattern. J Mol Biol. 1975 Apr 5;93(2):123–138. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90123-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne H. B., Nabedryk-Viala E. The conformation of membrane-bound and detergent-solubilised bovine rhodopsin. A comparative hydrogen-isotope exchange study. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Aug 15;89(1):81–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb20898.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne H. B., Sardet C., Michel-Villaz M., Chabre M. Structural study of rhodopsin in detergent micelles by small-angle neutron scattering. J Mol Biol. 1978 Aug 5;123(2):177–206. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90320-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne H. B. The hydrophobic heart of rhodopsin revealed by an infrared 1H-2H exchange study. FEBS Lett. 1977 Dec 15;84(2):217–220. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80691-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothschild K. J., Clark N. A. Polarized infrared spectroscopy of oriented purple membrane. Biophys J. 1979 Mar;25(3):473–487. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85317-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saibil H., Chabre M., Worcester D. Neutron diffraction studies of retinal rod outer segment membranes. Nature. 1976 Jul 22;262(5566):266–270. doi: 10.1038/262266a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sardet C., Tardieu A., Luzzati V. Shape and size of bovine rhodopsin: a small-angle x-ray scattering study of a rhodopsin-detergent complex. J Mol Biol. 1976 Aug 15;105(3):383–407. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90100-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shichi H., Shelton E. Assessment of physiological integrity of sonicated retinal rod membranes. J Supramol Struct. 1974;2(1):7–16. doi: 10.1002/jss.400020103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stubbs G. W., Smith H. G., Jr, Litman B. J. Alkyl glucosides as effective solubilizing agents for bovine rhodopsin. A comparison with several commonly used detergents. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Feb 19;426(1):46–56. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90428-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Susi H., Timasheff S. N., Stevens L. Infrared spectra and protein conformations in aqueous solutions. I. The amide I band in H2O and D2O solutions. J Biol Chem. 1967 Dec 10;242(23):5460–5466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timasheff S. N., Susi H., Stevens L. Infrared spectra and protein conformations in aqueous solutions. II. Survey of globular proteins. J Biol Chem. 1967 Dec 10;242(23):5467–5473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma S. P., Wallach D. F. Effects of cholesterol on the infrared dichroism of phosphatide multibilayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Dec 13;330(2):122–131. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90216-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worcester D. L. Structural origins of diamagnetic anisotropy in proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5475–5477. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




