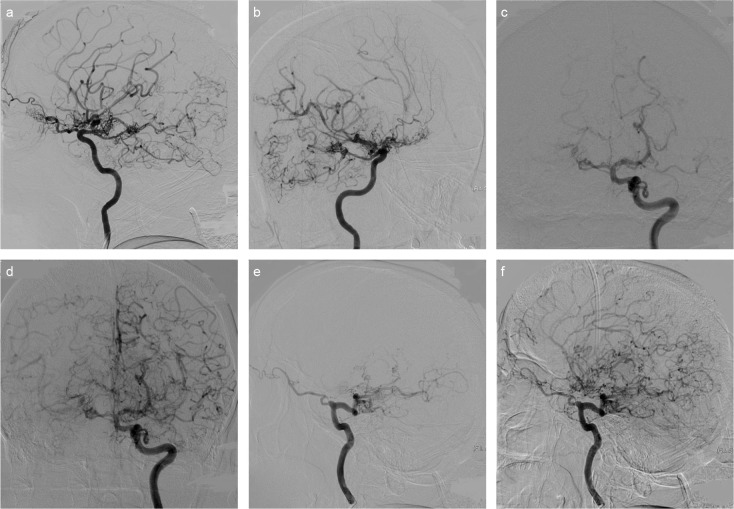
FIG. 2. a–f.
Vascular tissue contingent with Moyamoya vessels in lateral projection right ICA injection (a) and 45 degree right anterior oblique position (b). Also noted is the calibre reduction on the right ICA supraclinoid segment and the view belonging to the pial collaterals on the right MCA and PCA distal branches. The left MCA and the left ACA have been totally occluded in the early arterial phase in the left ICA injection in Town projection. It is also noted that the calibre of the supraclinoid segment of the left ICA has become thinner compared to the other ICA segments and shows irregularity (c). The same projection also demonstrates that both ACA and MCA branches show retrograde filling with pial collaterals in the late arterial phase. And moreover, there has been significant dilation of both PComAs (d). In the lateral position, the left MCA and ACA are totally occluded in the early arterial phase, and the left PComA is significantly dilated and fills with the distal basilar and PCA (e). There are bilateral ACA and MCA branches that present pial collateral and retrograde filling on ACA and MCA distal branches in the late arterial phase in the same projection. Additionally, Moyamoya vessels are present around PCA, ACA, and MCA branches (f). (ACA: Anterior cerebral artery, ICA: internal carotid artery, MCA: middle cerebral artery, PCA: posterior cerebral artery, PComA: posterior communicating artery).