Abstract
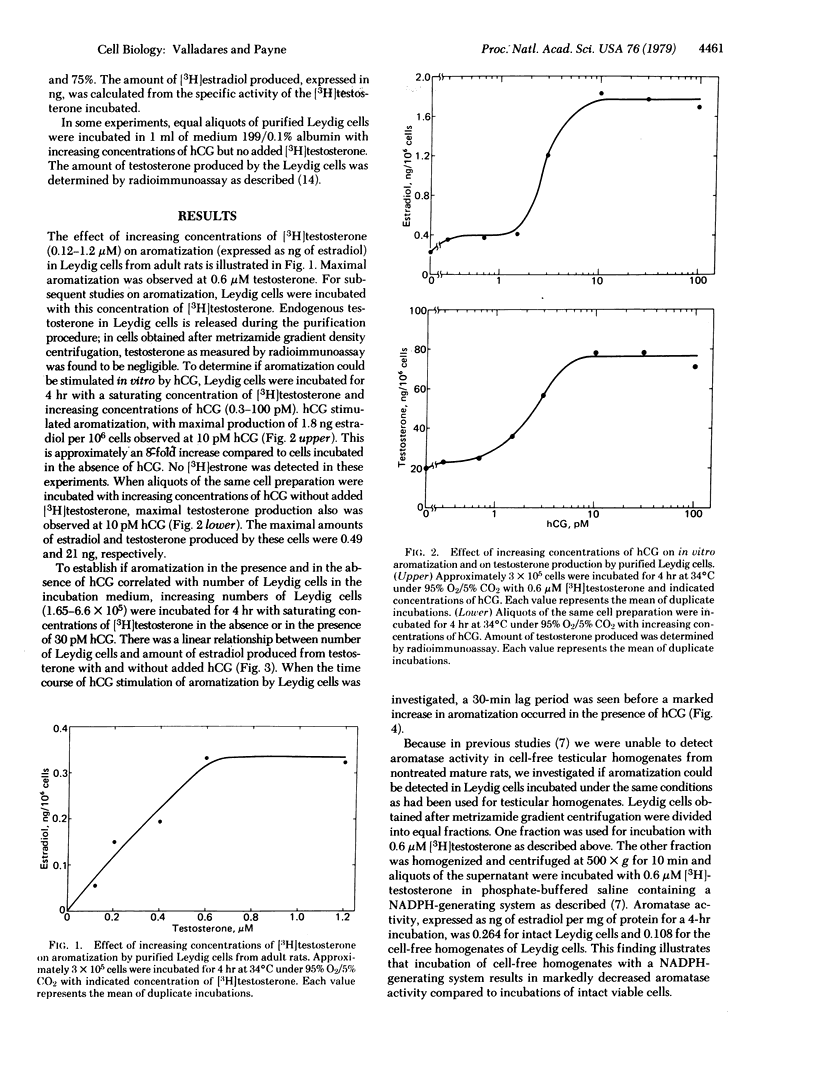
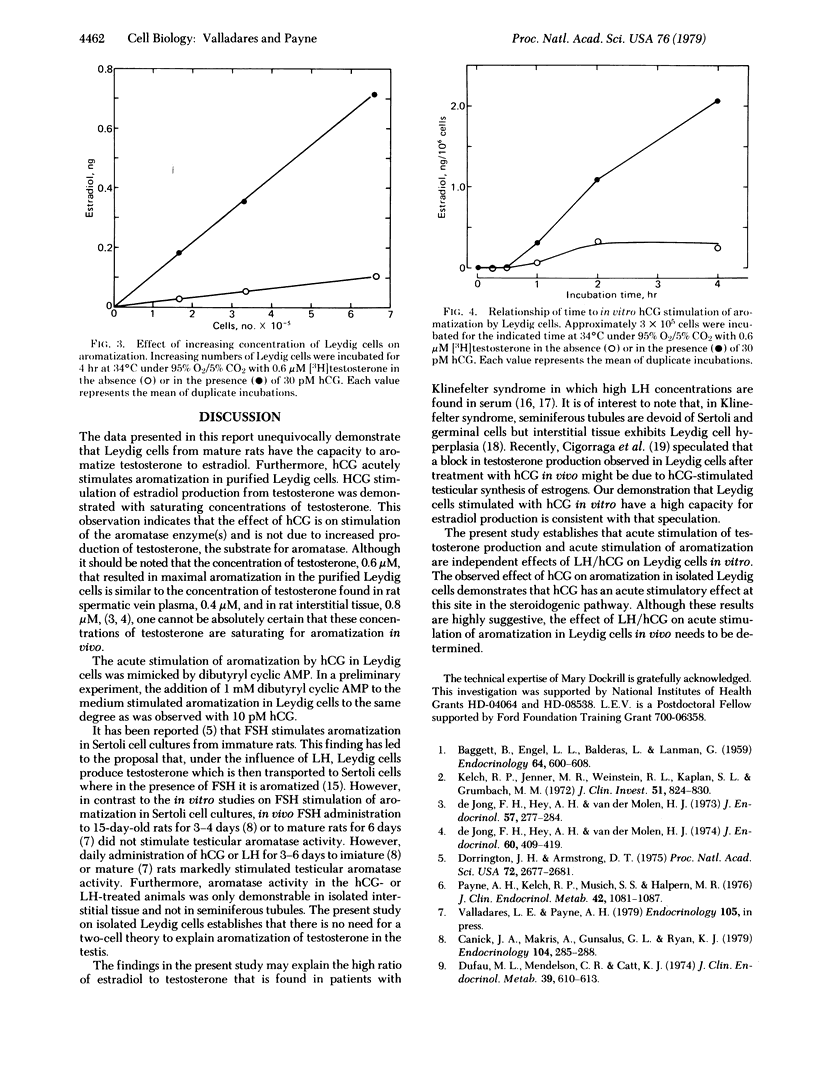
Aromatization of testosterone in Leydig cells purified from mature rat testes was assessed. Leydig cells incubated for 4 hr with increasing concentrations of [3H]testosterone. At saturating concentrations of testosterone, human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) acutely stimulated aromatization. This stimulation was first observed at 1 hr, an 8-fold increase being found during a 4-hr incubation. The maximal amount of estradiol produced at saturating concentrations of testosterone and hCG was 1.8 ng per 10(6) cells. These results demonstrate that purified Leydig cells have a high capacity for aromatization and that hCG can acutely stimulate aromatization independently of stimulating testosterone synthesis in vitro.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAGGETT B., ENGEL L. L., BALDERAS L., LANMAN G. Conversion of C14-testosterone to C14-estrogenic steroids by endocrine tissues. Endocrinology. 1959 Apr;64(4):600–608. doi: 10.1210/endo-64-4-600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canick J. A., Makris A., Gunsalus G. L., Ryan K. J. Testicular aromatization in immature rats: localization and stimulation after gonadotropin administration in vivo. Endocrinology. 1979 Feb;104(2):285–288. doi: 10.1210/endo-104-2-285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cigorraga S. B., Dufau M. L., Catt K. J. Regulation of luteinizing hormone receptors and steroidogenesis in gonadotropin-desensitized leydig cells. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 25;253(12):4297–4304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conn P. M., Tsuruhara T., Dufau M., Catt K. J. Isolation of highly purified Leydig cells by density gradient centrifugation. Endocrinology. 1977 Aug;101(2):639–642. doi: 10.1210/endo-101-2-639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorrington J. H., Armstrong D. T. Follicle-stimulating hormone stimulates estradiol-17beta synthesis in cultured Sertoli cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2677–2681. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorrington J. H., Fritz I. B., Armstrong D. T. Control of testicular estrogen synthesis. Biol Reprod. 1978 Feb;18(1):55–64. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod18.1.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dufau M. L., Mendelson C. R., Catt K. J. A highly sensitive in vitro bioassay for luteinizing hormone and chorionic gonadotropin: testosterone production by dispersed Leydig cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1974 Sep;39(3):610–613. doi: 10.1210/jcem-39-3-610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forti G., Giusti G., Borghi A., Pazzagli M., Fiorelli G., Cabresi E., Mannelli M., Bassi F., Giannotti P., Fusi S. Klinefelter's syndrome: a study of its hormonal plasma pattern. J Endocrinol Invest. 1978 Apr;1(2):149–154. doi: 10.1007/BF03350363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelch R. P., Jenner M. R., Weinstein R., Kaplan S. L., Grumbach M. M. Estradiol and testosterone secretion by human, simian, and canine testes, in males with hypogonadism and in male pseudohermaphrodites with the feminizing testes syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1972 Apr;51(4):824–830. doi: 10.1172/JCI106877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulsen C. A., Gordon D. L., Carpenter R. W., Gandy H. M., Drucker W. D. Klinefelter's syndrome and its variants: a hormonal and chromosomal study. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1968;24:321–363. doi: 10.1016/b978-1-4831-9827-9.50013-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne A. H., Kawano A., Jaffe R. B. Formation of dihydrotestosterone and other 5 alpha-reduced metabolites by isolated seminiferous tubules and suspension of interstitial cells in a human testis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1973 Sep;37(3):448–453. doi: 10.1210/jcem-37-3-448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne A. H., Kelch R. P., Murono E. P., Kerlan J. T. Hypothalamic, pituitary and testicular function during sexual maturation of the male rat. J Endocrinol. 1977 Jan;72(1):17–26. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0720017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne A. H., Kelch R. P., Musich S. S., Halpern M. E. Intratesticular site of aromatization in the human. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1976 Jun;42(6):1081–1087. doi: 10.1210/jcem-42-6-1081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiebe J. P. Steroidogenesis in rat leydig cells: changes in activity of 5-ane and 5-ene 3beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases during sexual maturation. Endocrinology. 1976 Feb;98(2):505–513. doi: 10.1210/endo-98-2-505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Jong F. H., Hey A. H., van der Molen H. J. Effect of gonadotrophins on the secretion of oestradiol- and testosterone by the rat testis. J Endocrinol. 1973 May;57(2):277–284. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0570277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Jong F. H., Hey A. H., van der Molen H. J. Oestradiol-17 beta and testosterone in rat testis tissue: effect of gonadotrophins, localization and production in vitro. J Endocrinol. 1974 Mar;60(3):409–419. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0600409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


