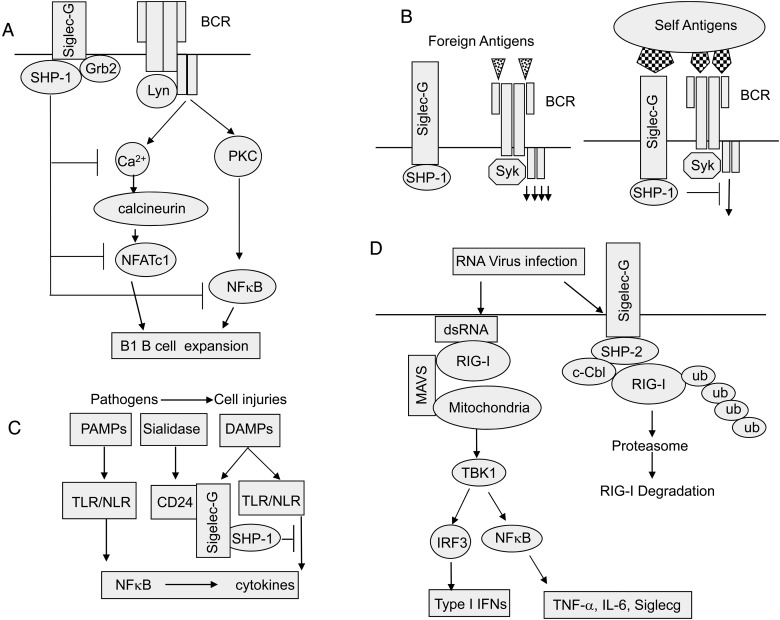
Fig. 2.
Siglec-G in adaptive and innate immunity. (A) Regulation of B1a B-cell proliferation and BCR signaling by Siglec-G. Siglec-G dampens the calcium signal on B1 cells and inhibits the activity of the transcription factor NFATc1 and NFκB by recruiting the ITIM-binding protein SHP-1 or Grb2. (B) Regulation of B-cell activation and tolerance. Self-antigens are expressed on cells with abundance of Siglec-G ligands and thus likely engage both BCR and Siglec-G. In contrast, foreign antigens are presented to B cells in the absence of Siglec-G ligands. (C) Siglec-G represses host response to DAMPs unless its ligand CD24 is desialylated by bacterial sialidase. (D) Siglec-G suppresses type I IFN production by promoting c-Cbl-mediated ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of RIG-I.