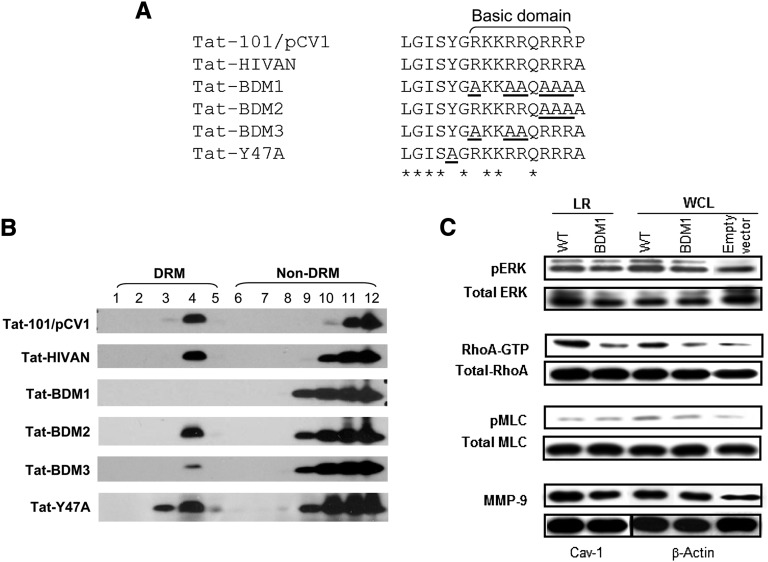
Figure 5.
Arginines located in the basic domain are essential for targeting Tat to the LRs in cultured podocytes. (A) Several mutations were introduced in the basic domain of the WT Tat isolated from a child with HIVAN (Tat-HIVAN) to generate different Tat BDMs named for the purpose of this study: Tat-BDM1, Tat-BDM2, Tat-BDM3, and Tat-Y47A (mutation introduced in the putative cholesterol recognition consensus sequence). The Tat-101 control gene derived from the HIV-1 cDNA clone pCV1 (Supplemental Figure 2) carries the RDG motif, which is missing in Tat-HIVAN and all the other Tat BDMs. All these sequences were aligned using the Clustal Omega multiple sequence alignment program. Residues aligned identical are marked with an asterisk. Mutated residues are underlined. (B) Podocytes were transiently transfected with Tat-101/pCV1, Tat-HIVAN, Tat-HIVAN BDMs, or Tat-HIVAN-Y47A mutant. Cells were lysed with Triton X-100 and fractionated using a sucrose gradient flotation assay. FLAG-tagged Tat was detected by Western blot using the anti-FLAG antibody. (C) Western blot analyses showing changes in pERK, Rho-A, pMLC, and MMP-9 expression in isolated LRs and whole-cell lysates (WCLs) extracted from cultured podocytes transfected with WT Tat and Tat-mutated in BDM1 and the empty vector. GTP, guanosine triphosphate.