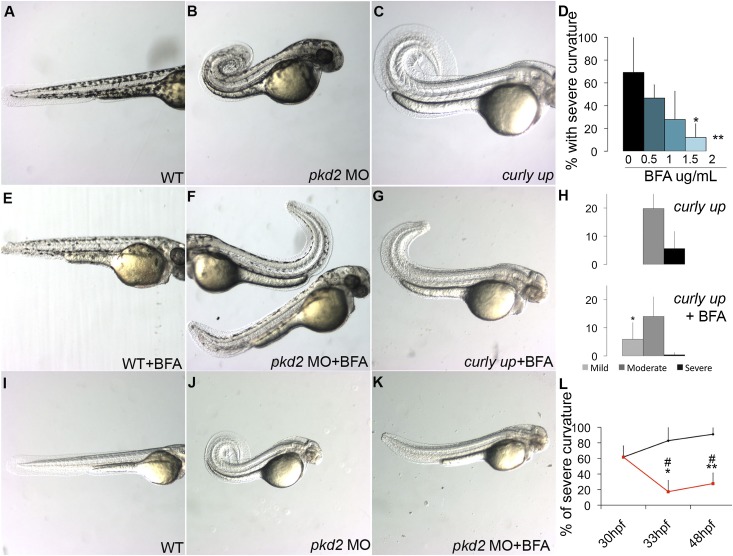
Figure 4.
BFA treatment prevents dorsal axis curvature in pkd2-deficient embryos. (A) Wild-type embryo, (B) pkd2 morphant, and (C) cup embryo at 48 hpf. (E–G) Treatment with BFA (E) does not induce curvature in wild-type embryos but reduces dorsal axis curvature in (F) pkd2 morphants and (G) cup embryos when added at 2 μg/ml at 24 hpf. (D) Percentage of embryos with severe curvature in pkd2 morphants at 48 hpf (n=3 independent experiments). (H) Percentage of embryos with mild curvature (light gray bars), moderate curvature (dark gray bars), and severe curvature (black bars) in cup embryos (upper panel) and BFA-treated cup embryos (lower panel) at 48 hpf (n=3 independent experiments). pkd2 morphants (n=71); pkd2 morphants+BFA (n=57 at 0.5 μg/ml, n=75 at 1 μg/ml, n=73 at 1.5 μg/ml, n=60 at 2 μg/ml); cup mutants (n=298); cup mutants+BFA (n=222). The increase in pkd2 morphant embryos with mild curvature in the BFA sample was statistically significant (*P=0.05). (I) Wild-type embryo, (J) pkd2 morphant, and (K) BFA-treated pkd2 morphant at 48 hpf. (L) Percentage of embryos with moderate and severe curvature at 48 hpf in pkd2 morphants (black line) and pkd2 morphants treated with BFA at 30 hpf (red line). The quantification of two independent experiments at 33 hpf and three independent experiments at 48 hpf shows that BFA treatment can rescue preexisting curvature in pkd2 morphants. Wild type (n=270 at 30 hpf, n=73 at 33 hpf, n=71 at 48 hpf); pkd2 morphants (n=210 at 30 hpf, n=65 at 33 hpf, n=57 at 48 hpf); wild type+BFA (n=63 at 30 hpf, n=57 at 48 hpf); pkd2 morphants+BFA (n=68 at 33 hpf, n=53 at 48 hpf). *Percentage with severe curvature in BFA treated at 33 and 48 hpf was significantly different from untreated pkd2 morphants at 33 hpf; **percentage with severe curvature in BFA treated at 33 and 48 hpf was significantly different from untreated pkd2 morphants at 48 hpf; #percentage with severe curvature in BFA treated at 33 and 48 hpf was significantly different from the starting time point in both cases. MO, morpholino oligo–injected; WT, wild-type.