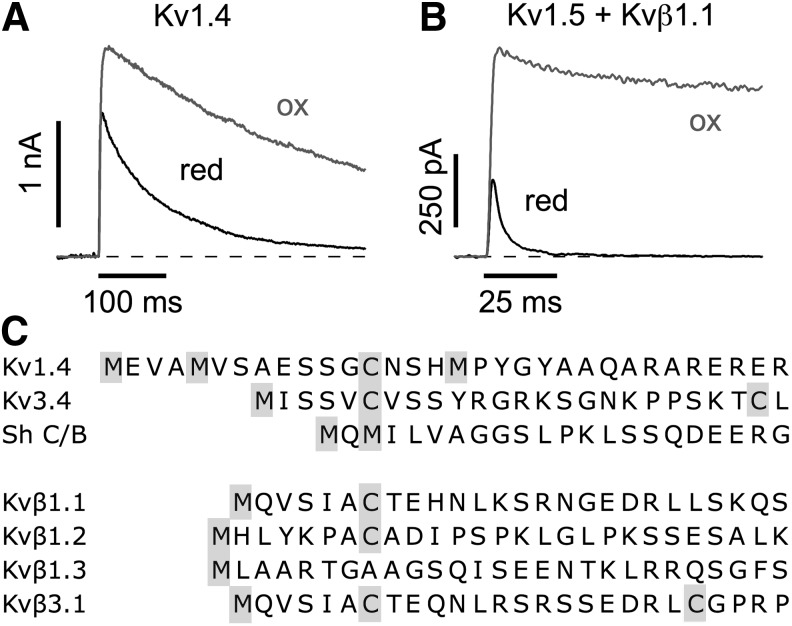
FIG. 5.
N-type inactivation. (A, B) Current traces at 40 mV from Xenopus oocytes expressing Kv1.4 (A) and Kv1.5+Kvβ1.1 (B) in the on-cell mode (black) and upon excision to the inside-out configuration (gray) indicating the redox dependence of fast inactivation. (C) Alignment of N-terminal sequences of α-subunits (top) and Kvβ subunits (bottom) that induce N-type inactivation. Cysteine (C) and methionine (M) residues are highlighted.