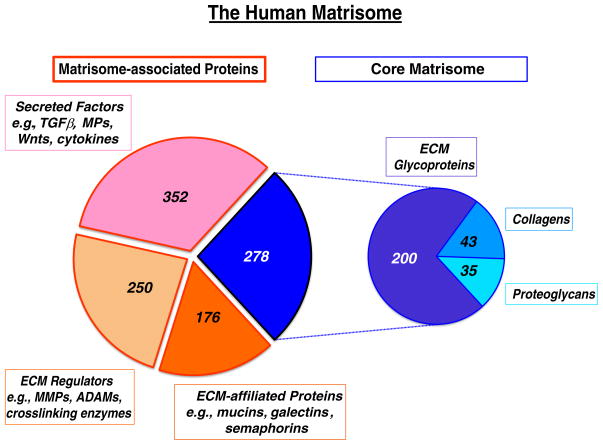
Fig. 1.
The human matrisome and its subcategories.
The core matrisome comprises three subcategories; ECM glycoproteins, collagens and proteoglycans, in each case defined by their domain structures (see text). All of these proteins are believed to assemble into extracellular matrices of one sort or another.
The three main subcategories of matrisome-associated proteins are more inclusively defined – they include proteins known to associate with assembled ECM as well as related proteins that may or may not – all were included to ensure their capture in “omic” screens of various sorts.
The secreted protein category includes a list of growth factors, cytokines and other secreted proteins — some are known to bind to ECM at least part of the time; others are included in the expectation that many of them will also be discovered to bind to ECM.
The ECM regulator category includes proteases, protease inhibitors and ECM crosslinking enzymes. Again, many are known to bind to and modify ECM proteins and structures in important ways — their homologs are likely also to do so and have been included for completeness.
The final category, designated “ECM-affiliated” includes protein families that some scientists (but not others) may consider as ECM proteins (e.g., mucins, C-type lectins, syndecans, glypicans), some that could be viewed as secreted factors but which also associate with solid-phase complexes (e.g., semaphorins and their homologous receptors, plexins, collagen-related proteins such as C1q and homologs) and a few families that appear repeatedly in ECM-enriched preparations for currently unknown reasons (e.g., annexins, galectins). Complete lists of the proteins in each subcategory for both human and mouse, together with gene and protein identifiers as well as protein sequence files are given in Naba et al. 2012 and at http://web.mit.edu/hyneslab/matrisome/ and summary tables are given in Hynes and Naba (2012).