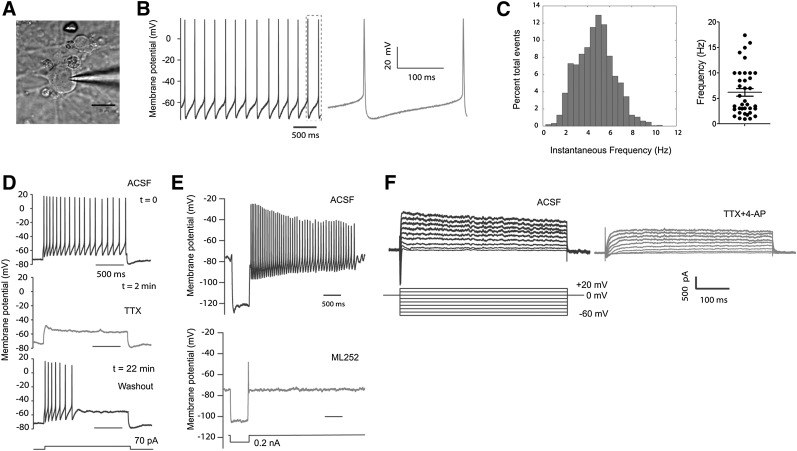
Figure 6.
Electrophysiological properties of Atoh1-induced dopaminergic (DA) neurons. (A): Differential interference contrast image of a patched Atoh1-induced DA neuron. Scale bar = 20 μm. (B, C): Atoh1-induced DA neurons derived from Atoh1-iPSCs showed spontaneous spiking activity. This cell has a resting membrane potential of −65 mV (B) (a zoomed view is shown in the right panel) and an average spiking frequency of 4.8 Hz (C) (left panel). The spontaneous spiking frequencies from 37 neurons were plotted in the right panel of (C) with the means ± SEM marked inside. (D): Whole cell current-clamp recording of action potentials evoked by 70 pA current injection (top panel). Action potentials were suppressed by sodium channel blocker (TTX) (middle panel). Action potentials recovered after TTX withdrawal (bottom panel). (E): An hyperpolarized injection of current (0.2 nA) evoked hyperpolarization and rebound tonic spiking. A typical hyperpolarization sag was observed in the upper panel, which was dampened by ML252 (5 µM, a KCNQ2 inhibitor, lower panel). (F): Voltage-clamp recording of Atoh1-induced neurons. Depolarized sodium and potassium currents were evoked by elevation the membrane potential to different levels (left panel). Both sodium and potassium currents were attenuated by sodium and potassium channel inhibitors (TTX [0.5 µM] and 4-AP [25 µM], respectively). Abbreviations: ACSF, artificial cerebrospinal fluid; TTX, tetrodotoxin.