Fig. 1.
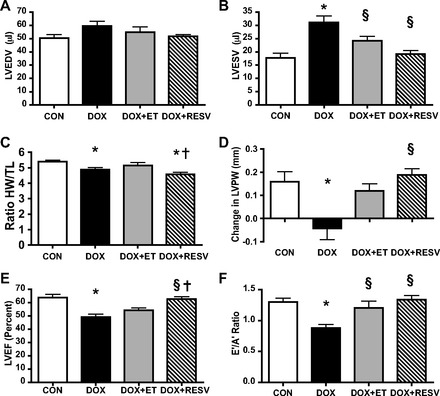
Exercise training (ET) and resveratrol (RESV) both attenuate doxorubicin (DOX)-induced cardiotoxicity. Echocardiography analysis of sedentary saline-injected controls (CON), DOX, DOX + ET, and DOX + RESV mice; left-ventricular (LV) end-diastolic volume (LVEDV) (A); LV end-systolic volume (LVESV) (B); ratio of heart weight-to-tibia length (HW/TL) (C); change in LV posterior wall thickness (LVPW) (D); LV ejection fraction (LVEF) (E); and the E′/A′ ratio (F). Values are means ± SE. (n = 9–10). *P < 0.05, value for difference vs. CON group; §P < 0.05, value for DOX vs. DOX + ET or DOX + RESV groups; †P < 0.05, value for DOX + ET vs. DOX + RESV groups.
