Figure 5. Acrolein treatment inhibits nucleotide excision repair and base excision repair in human urothelial cells.
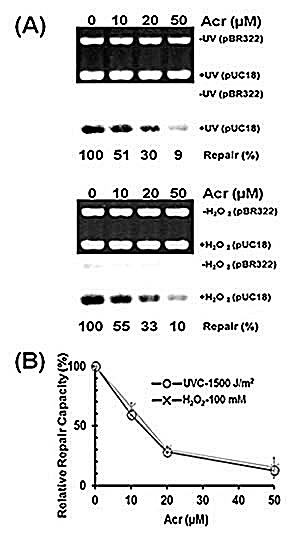
Immortalized human urothelial (UROtsa) cells were treated with 0, 10, 20, or 50 μM acrolein for 1 h at 37 °C. The nucleotide excision and base excision repair capacity in these cells were determined by (A) an in vitro DNA damage dependent repair synthesis assay using UV-irradiated or H2O2 modified pUC18 plasmid DNA as substrates, and (B) a host cell reactivation assay using UV-irradiated or H2O2 modified luciferase plasmid pGL3 as substrates, as previously described (13, 26).
