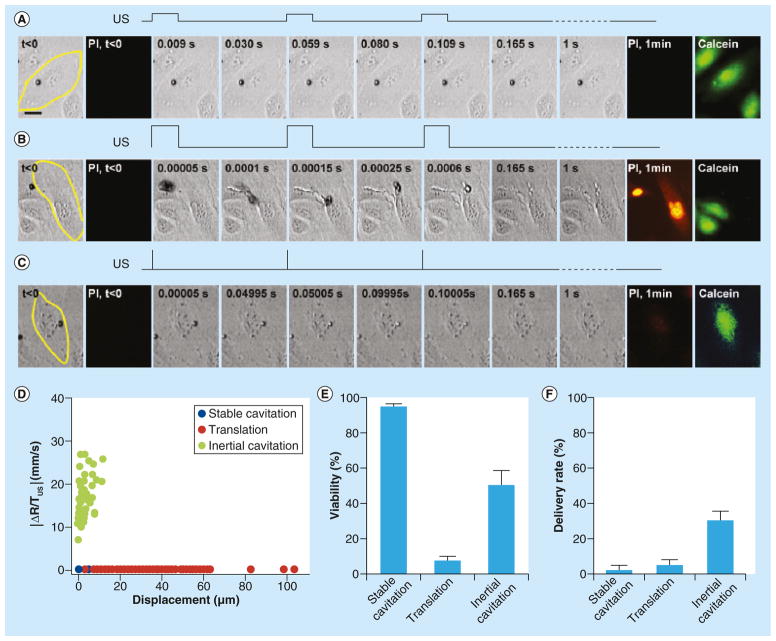
Figure 3. Three typical types of bubble dynamics in application circumstances driven by different ultrasound conditions.
These are featured by (A) stable cavitation, (B) translation, and (C) inertial cavitation. The PI images show delivery from the extracellular space, while the post-US calcein images show cellular viability. (D) When characterized by change in bubble radius per unit time (ΔR/TUS) versus total length of bubble displacement, the three groups are fairly well-distinguished. (E & F) The third type, inertial (transient) cavitation, driven by short pulse and high pressure, led to the highest delivery efficiency with the highest delivery rate and reasonably high viability.
US: Ultrasound.
Reproduced with permission from [54].