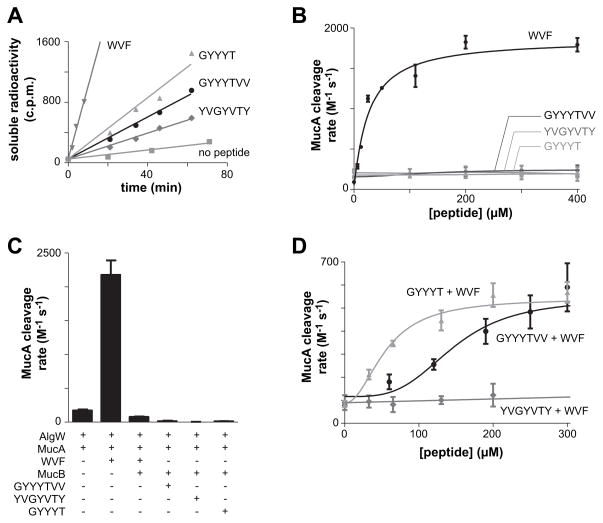
Fig. 4. CupB5 peptides relieve MucB inhibition of MucA cleavage by AlgW.
(A) Cleavage of 35S-labelled MucA (20 μM) by AlgW (0.5 μM trimer) was assayed by the time-dependent release of acid-soluble peptides in the presence of either the OMP-like WVF peptide (400 μM), the wild-type GYYYT or GYYYTVV CupB5 peptides (400 μM), the sequence-scrambled YVGYVTY peptide (400 μM), or a buffer control. (B) Second-order rate constants for MucA cleavage were determined by incubating 35S-labelled MucA (20 μM) and AlgW (0.5 μM trimer) with different concentrations of WVF or CupB5 peptides and measuring the time-dependent increase in acid-soluble products. Rates were divided by the MucA and AlgW concentrations to determine activity. Lines are fits to the equation activity = basal + stimulated/(1+(Kact/[peptide])h). Values are averages ± SEM (n=2). (C) Second-order rate constants for cleavage of 35S-MucA (20 μM) by AlgW (0.5 μM trimer) were determined as described in panel B in the presence of different combinations of WVF peptide (110 μM), MucB (25 μM dimer), and wild-type or scrambled CupB5 peptides (405 μM). Values are averages of two or more independent trials ± SEM. (D) Second-order rate constants for cleavage of 35S-MucA (20 μM) by AlgW (0.5 μM trimer) and WVF peptide (150 μM) were determined in the presence of increasing concentrations of the GYYYT, GYYYTVV, or sequence-scrambled YVGYVTY peptides. Lines are fits to the Hill equation: rate = basal + Vmax/(1 + (Ks/[peptide])h). For GYYYT, Ks was 55 ± 13 μM and h was 2.1 ± 0.9. For GYYYTVV, Ks was 143 ± 31 μM and h was 3.5 ± 2.2.