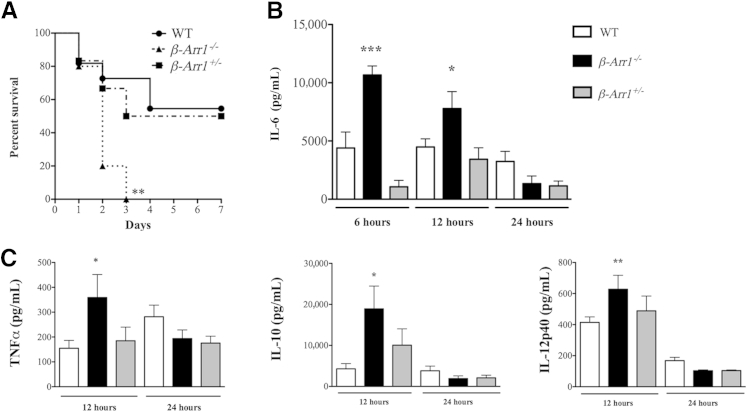
Figure 1.
Role of β-arrestin-1 (βArr1) in sepsis-induced mortality and inflammation. A: Wild-type (WT), βarr1 knockout (KO) (β-Arr1−/−), and βArr1 heterozygous (β-Arr1+/−) mice were subjected to 16-guage needle single-puncture surgery and observed for mortality over 7 days. B and C: Mice from the different genotypes were subjected to cecal ligation and puncture as indicated in A, and plasma cytokine concentrations in septic mice determined at the indicated time points after surgery. n = 10 to 12 mice for each genotype (A); n = 8 to 14, with data pooled from at least two independent experiments (B and C). Error bars on the figure denote SEM. ∗∗P < 0.01 compared to WT by log-rank (Mantel Cox) test (A); ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, and ∗∗∗P < 0.001 compared to WT using t-test (B and C).