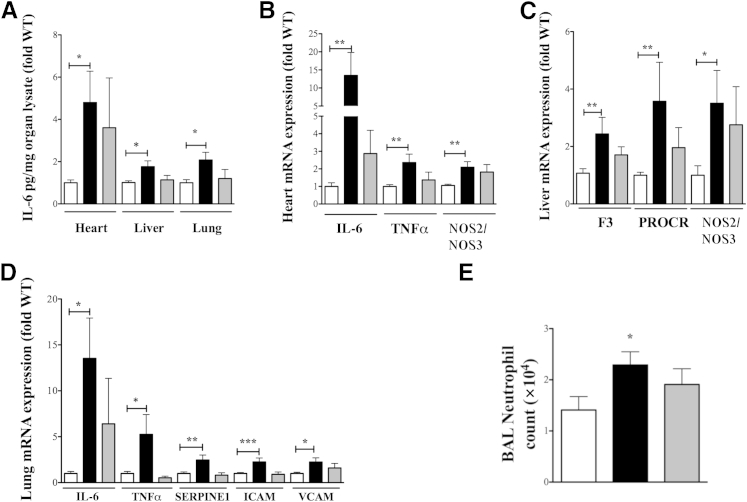
Figure 3.
Role of β-arrestin-1 (βArr1) in sepsis-induced organ inflammation. A: Wild-type (WT; white bars), βArr1 knockout (β-Arr1−/−; black bars), and βArr1 heterozygous (β-Arr1+/−; gray bars) mice were subjected to 16G-single puncture surgery, and the indicated organs were collected at defined time points for analysis. IL-6 levels (pg/mg) in organ lysates (determined by ELISA) from septic mice 12 hours after surgery. B–D: Quantitative real-time PCR analysis of inflammatory mediators in heart (B), liver (C), and lung tissue (D) from septic mice 12 hours after surgery. E: Total number of neutrophils as determined by flow cytometry isolated from bronchoalveolar lavage of septic mice 24 hours after surgery. mRNA expression was normalized to HPRT before converting to fold WT. Protein and RNA data are represented as fold WT and are pooled from at least two independent experiments. n = 8 to 17 for each genotype. Error bars denote SEM. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, and ∗∗∗P < 0.001 using Student's t-test.