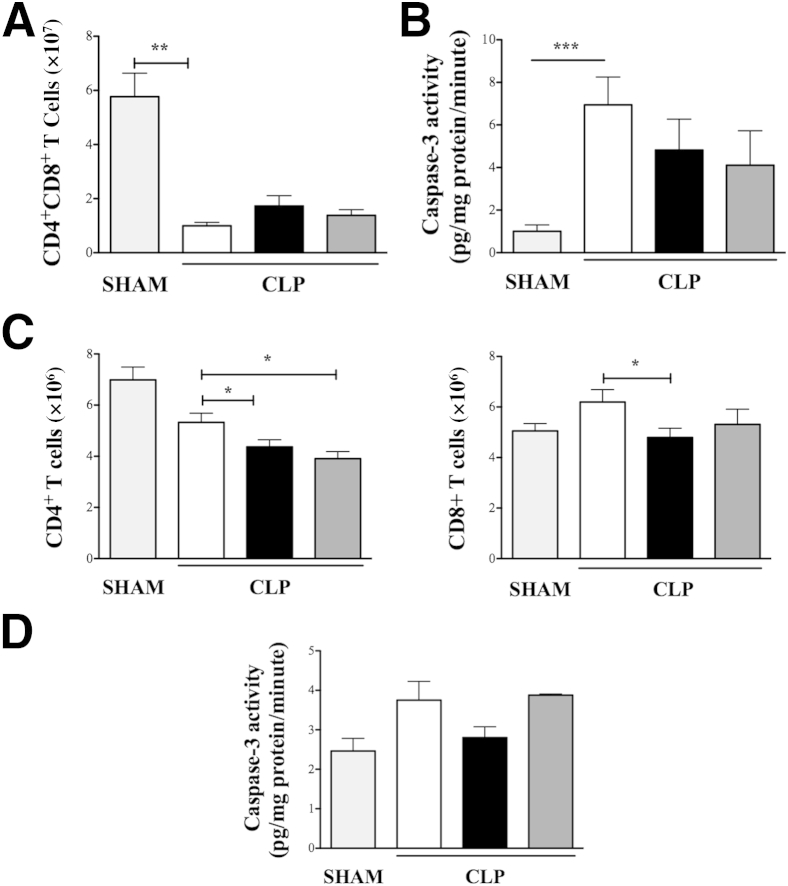
Figure 5.
Role of β-arrestin-1 (βArr1) in sepsis-induced lymphocyte apoptosis. Wild-type (WT; white bars), βArr1 knockout (β-Arr1−/−; black bars), and βArr1 heterozygous (β-Arr1+/−; dark gray bars) mice were subjected to 16-guage needle single-puncture surgery, and thymus and spleen were collected 24 hours after surgery for the indicated parameters/analysis. A and B: CD4+CD8+ T cells in thymus as determined by flow cytometry (A) and caspase-3 activity in thymic lysates of septic mice as compared to WT/sham (light gray bars) (B). C and D: CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in spleen as determined by flow cytometry (C) and caspase-3 activity in splenic lysates from septic mice as compared to WT/sham (D). Data are pooled from at least three independent experiments for septic mice. n = 4 to 6 for sham and n = 10 to 19 for septic mice for each genotype (A–C); n = 4 to 5 (D). Error bars denote SEM. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, and ∗∗∗P < 0.001 using Student's t-test.