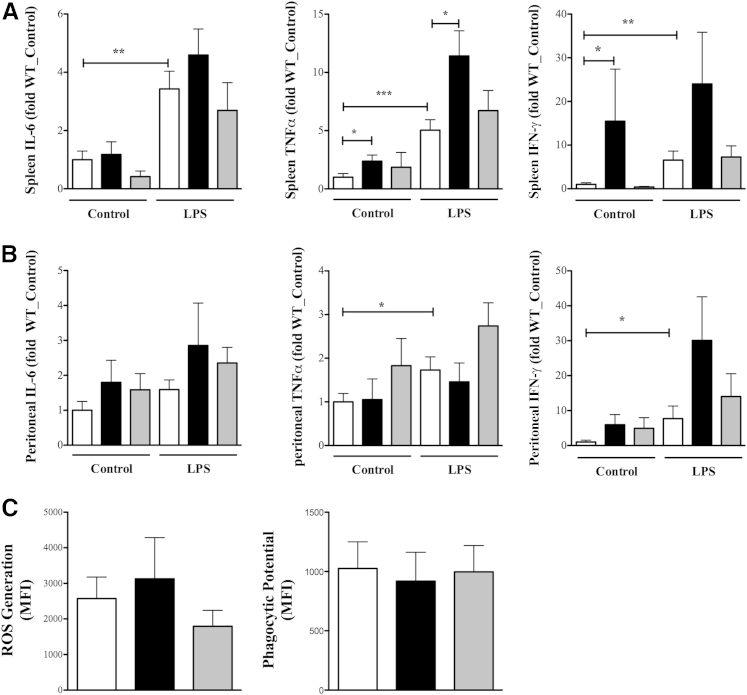
Figure 6.
Role of β-arrestin-1 (βArr1) in sepsis-induced immune-suppression. Wild-type (WT; white bars), βArr1 knockout (β-Arr1−/−; black bars), and βArr1 heterozygous (β-Arr1+/−; gray bars) mice were subjected to 16-guage needle single-puncture surgery, and spleen and peritoneal cells were collected 24 hours after surgery and processed. Cells were then plated and left untreated (control) or stimulated for 18 hours with 100 ng/mL lipopolysaccharide (LPS). A and B: Cytokine levels in the supernatants in splenocytes (A) and peritoneal cells (B) in control and LPS stimuli as determined by ELISA. Data are presented as fold change over WT control. C: Phagocytic potential and reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation in peritoneal cells from septic mice presented as mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) increase over controls. Data were pooled from three independent experiments. n = 8 to 10. Error bars denote SEM. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, and ∗∗∗P < 0.001 using Student's t-test (A and B).