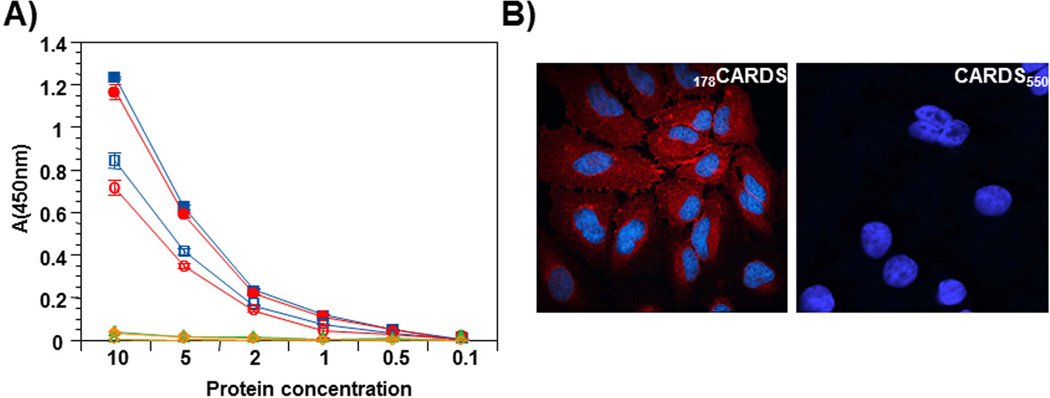
Fig. 4. Carboxy region of CARDS toxin mediates binding and internalization.
A) Comparison of binding and internalization of FL, selected C-terminal truncated CARDS toxin derivatives and 178CARDS toxin. FL toxin and its derivatives were purified as indicated in Experimental Procedures and biotin labeled. Binding: Proteins were incubated with HeLa cells for 1 h at 4°C. Subsequently, cells were washed and bound proteins were quantified as indicated in Experimental Procedures. Internalization: After 1 h incubation at 4°C, bound proteins (FL, selected C-terminal truncated CARDS toxin derivatives and 178CARDS toxin) were removed by washing, and cells were shifted to 37°C for 1 h with fresh medium. Then, cells were treated with MESNA to remove surface-bound, biotin-labeled CARDS toxin and its derivatives, and internalized proteins were quantified after permeabilizing cells as indicated in Experimental Procedures. Binding and internalization results of FL and variants of CARDS toxin are shown by closed and open symbols respectively. FL - square, 178CARDS - circle, CARDS249 - triangle and CARDS550 -diamond. B) Endocytosis of 178CARDS toxin and CARDS550 toxin. HeLa cells were treated with 140 pmol of 178CARDS toxin or CARDS550 toxin for 30 min at 4°C, washed to remove unbound toxins and shifted to 37°C for 1 h. Cell preparations were fixed and permeabilized with 0.1% Triton X-100, followed by incubation with anti-CARDS toxin rabbit primary antibodies. Cells were treated with AlexaFluor-633 conjugated anti-rabbit goat (polyclonal) secondary antibodies to detect cellular binding of CARDS toxin derivatives by confocal laser scanning microscopy. Cell nuclei were stained with DAPI.