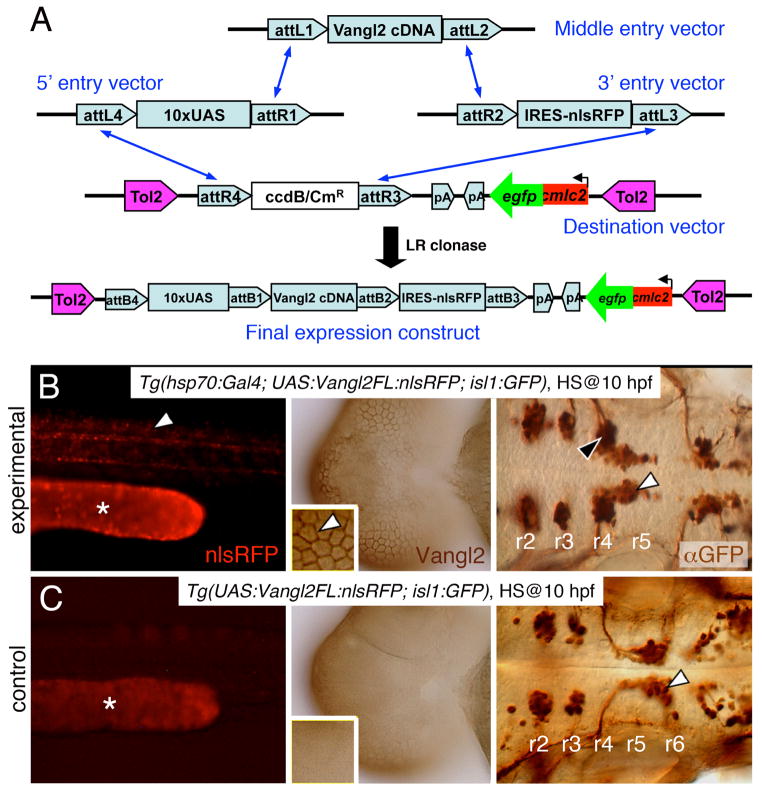
Figure 3. Stable heat shock-induced overexpression of Vangl2 FL causes defects in FBM neuron migration (dominant-negative phenotype).
(A) Schematic outlining the Gateway cloning strategy for generating Tol2 vectors for various Vangl2 constructs used to generate stable transgenic lines. (B) In triple transgenic 48 hpf Tg(hsp70:Gal4); Tg(UAS:Vangl2FL-nlsRFP); Tg(isl1:Gfp) experimental embryos heat shocked at 10 hpf, RFP-expressing cells (left panel, white arrowhead) were distributed broadly throughout the embryo. Myc-immunostaining (middle panel, brown) showed Vangl2 protein expressed on cell membranes (inset, white arrowhead). Importantly, anti-GFP immunostaining (right panel, brown) revealed that a majority of FBM neurons failed to migrate out of r4 (black arrowhead), while several neurons had migrated into r5 (white arrowhead). (C) By contrast, in double transgenic Tg(UAS:Vangl2FL-nlsRFP); Tg(isl1:Gfp) control embryos heat shocked at 10 hpf, RFP and Vangl2-expressing cells were absent, and FBM neurons migrated normally from r4 to r6 (white arrowhead). Asterisks in RFP panels in B and C indicate autofluorescence in the yolk tube.