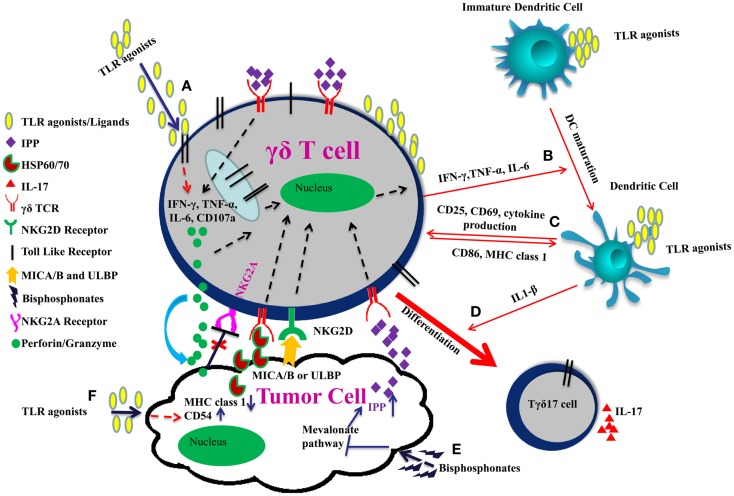
Figure 1.
Improving γδ T cell functions by TLRs in combinatorial therapy. (A) TLR agonists induce effector function of γδ T cells through IFN-γ, TNF-α, IL-6 secretion, and increased expression of CD107a. (B) IFN-γ, TNF-α, and IL-6 secreted by γδ T cells and TLR agonists promote the maturation of dendritic cell. (C) γδ T cells upregulate CD86 and MHC I expression on DCs and are themselves activated through up-regulation of CD25, CD69, and cytokine production thereby modulating each other’s function. (D) Co-stimulation of γδ T cells with TLR agonists and IL-1β secreted by dendritic cells promote their polarization toward IL17 producing cells. (E) γδ TCR also recognizes the specific molecular patterns such as IPP, which are induced upon inhibition of mevalonate pathway by bisphosphonates. Moreover, NKG2D receptor on γδ T cells recognizes MICA/B or ULBP expressed on tumor cells. This binding enhances release of perforins and granzymes by the γδ T cells leading to tumor cell lysis. (F) TLR agonists act as adjuvants and can induce CD54 expression and downregulation of MHC class 1 on tumor cells. Interaction between CD54 and its ligand CD11a/CD18 trigger effector functions in γδ T cells. Downregulation of MHC class 1 molecule on tumor cells result in reduced signaling through the inhibitory receptor NKG2A on γδ T cells, which enhances the cytotoxic potential of γδ T cell.