Figure 3. Effects of Flufenamic acid on several preparations.
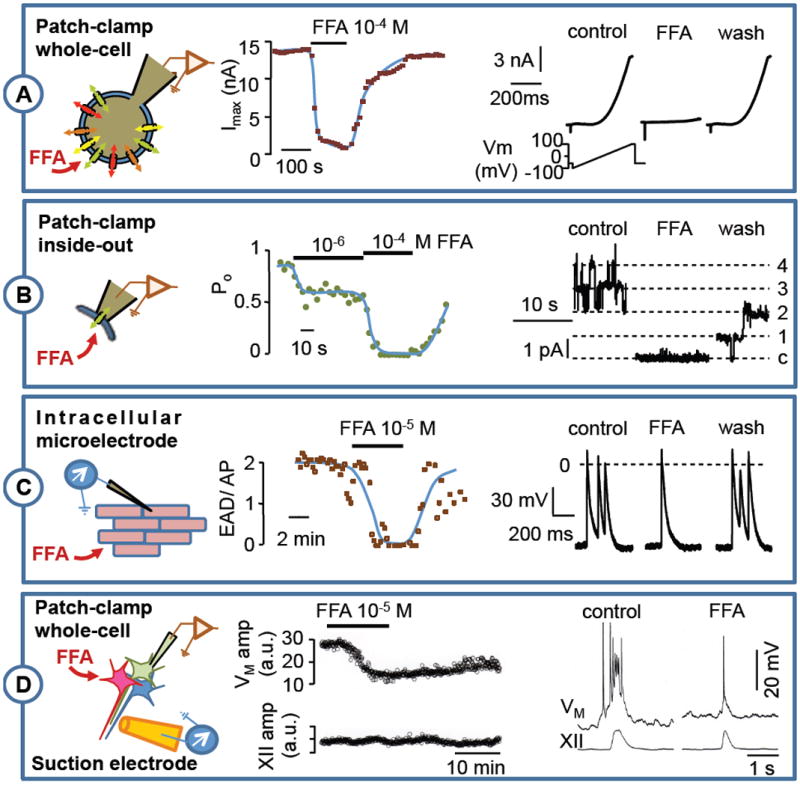
A: Inside-out patch-clamp recording of TRPM4 current on rat ventricular isolated myocyte (Vm = +40 mV). FFA produced a dose-dependent and reversible channel inhibition (see Guinamard et al. 2006-b for protocol). B: Action potential recorded by an intracellular microelectrode on isolated mouse ventricle submitted to a hypoxia and reoxygenation protocol (see Simard et al. 2012 for protocol). FFA superfusion reversibly reduced the number of early after depolarization by action potential (EAD/AP). C: Respiratory bursts recorded in rhythmogenic neurons of the preBötzinger complex (preBötC) as well as hypoglossal nerve root (XII) from neonatal mouse brainstem-slice preparations. Whole-cell patch-clamp recordings in preBötC neurons show that 100 μM FFA attenuates respiratory bursts at the whole-cell level by attenuating ICAN, but has a relatively mild affect motor output from the XII nerve root output (see Picardo et al. 2012 for protocol).
