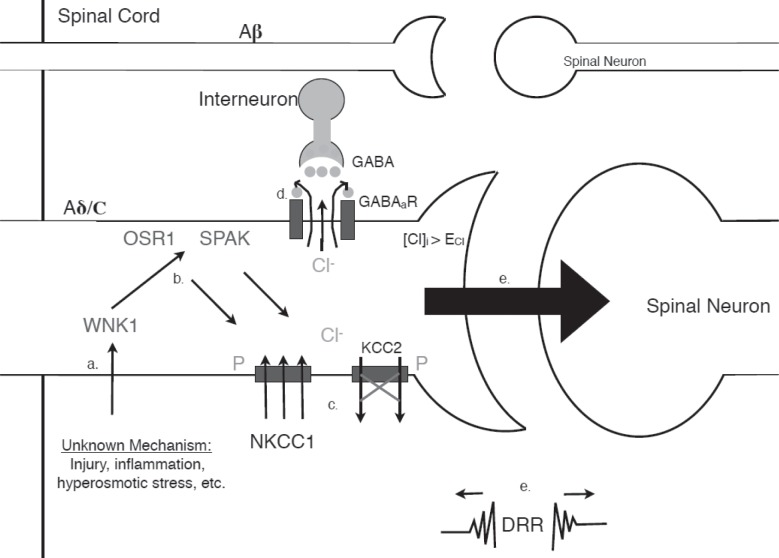
Fig. 1:
Hypothetical role of WNK1 in pathologic spinal cord signaling. In normal spinal cord signaling tactile information is processed by Aβ-fibers, and a presynaptically linked GABA-ergic interneuron causes PAD of nociceptive pathways. However, an unknown mechanism such as injury will a. cause phosphorylation of WNK1 which, b. phosphorylates OSR1 and SPAK which, c. phosphorylates the NKCC1 and KCC2 channels, activating and deactivating these channels, respectively. This leads to [Cl-]i >ECl.-, d. reversed GABA signaling, and e. activation of otherwise silent nociceptive pathways and antidromically conducted DRR, leading to hyperalgesia or allodynia.