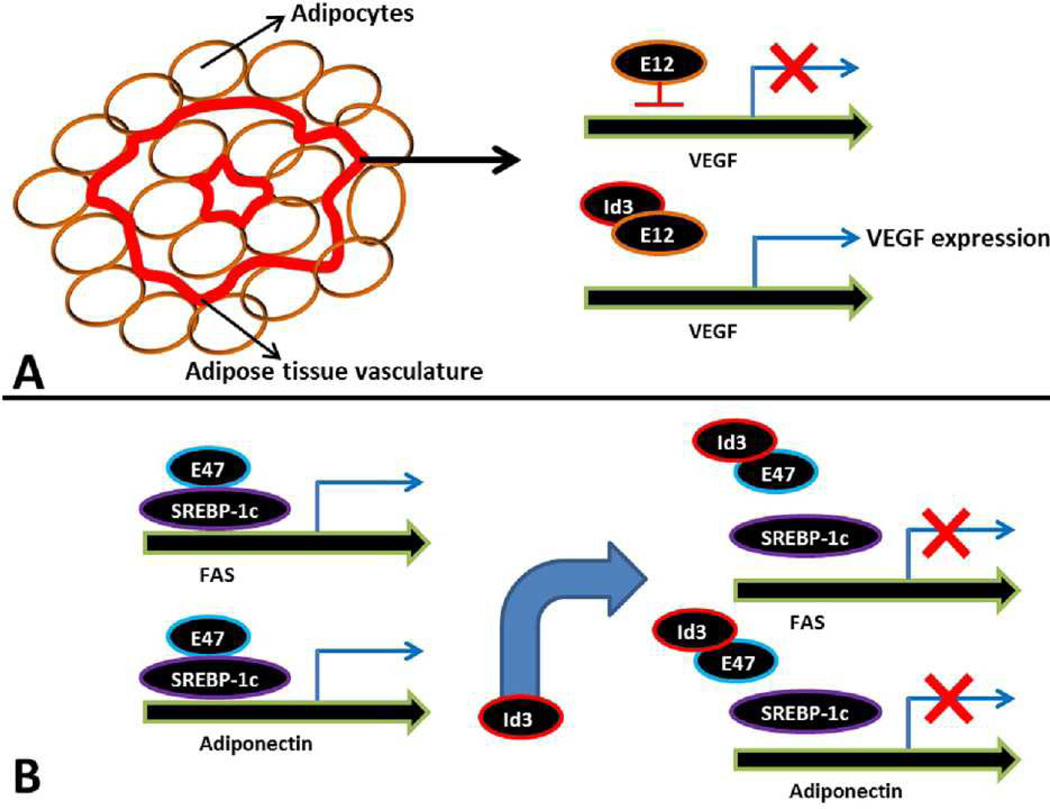
Figure 3.
(A) Possible mechanism describing the role of Id3 in adipose tissue vascularization during adipose tissue expansion. VEGF is essential for growth of blood vessels during visceral fat expansion. E12 functions as a transcriptional repressor of VEGF. Id3 promotes VEGF expression by interacting with and preventing E12 from binding to the VEGF promoter (54). (B). Possible mechanism showing the role of Id3 in adipose tissue-associated fatty acid and adipokine metabolism. E47 interacts with SREBP-1c, a positive regulator of FAS and adiponectin, and enhances SREBP-1c–mediated promoter activation. Id3 regulates SREBP-1c activity indirectly by interacting with E47. Id3/E47 interaction prevents E47 binding to the SREBP-1c leading to impaired activation of FAS and adiponectin promoters and their expression (58).