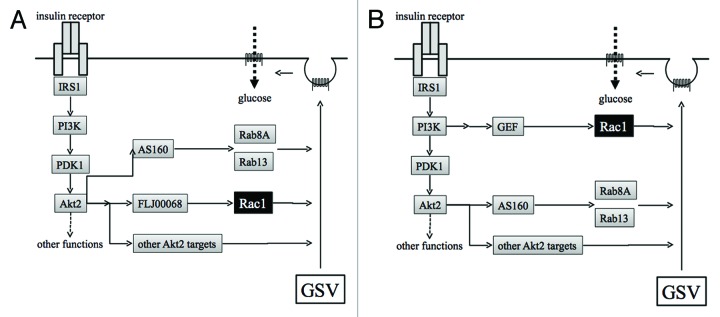
Figure 2. Proposed models for insulin-dependent signal transduction that stimulates exocytosis of GLUT4 from GSVs to the plasma membrane in skeletal muscle. (A) The insulin receptor, when occupied by insulin, stimulates a downstream kinase cascade composed of PI3K, PDK1, and Akt2. Akt2 acts as a master switch that regulates various signaling pathways necessary for GLUT4 translocation. Rac1 is also regulated downstream of Akt2. (B) Akt2 and Rac1 act independently in pathways bifurcated downstream of PI3K. GSV, GLUT4 storage vesicle; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase.
