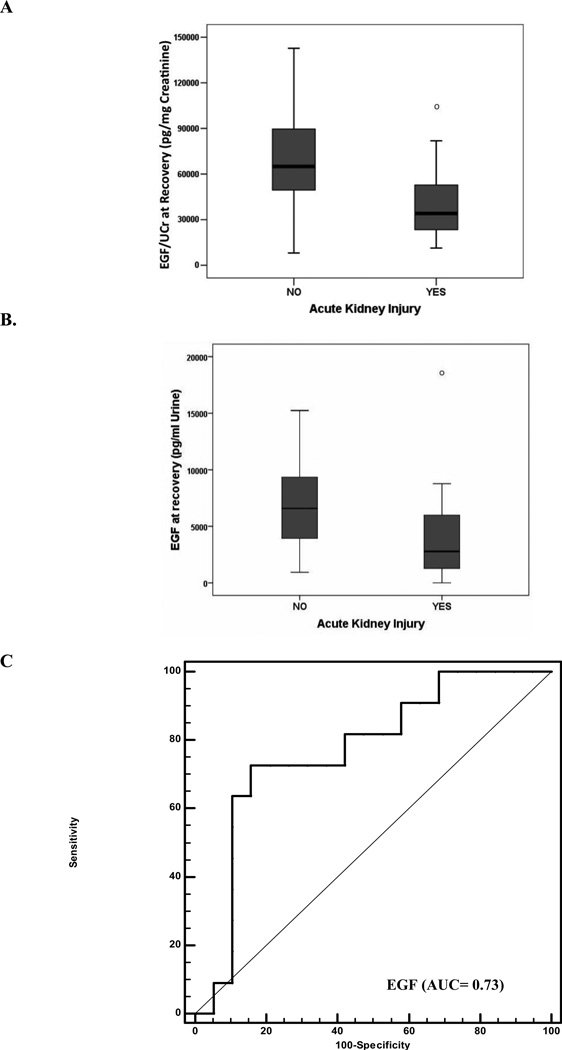
Fig. 5.
The urinary levels of Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF) at recovery are lower in newborns treated with Hypothermia (HT) or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) who developed acute kidney injury (AKI), when compared to those who did not develop AKI. Data represented as both (A) absolute values normalized for urinary creatinine (*p=0.014) and (B) concentration per mL of urine (*p= 0.03). Panel C shows a receiver operational characteristic (ROC) curve and the area under the curve (AUC) for EGF at recovery. Its predictive ability to detect AKI in a group of critically ill newborns treated with HT or ECMO, was assessed using control samples collected from newborns who did not develop AKI during the HT or ECMO treatments (assuming a 40% prevalence of AKI). The dashed reference line represents a ROC curve for a test with no discriminatory ability. The AUC for EGF is displayed on the graph.