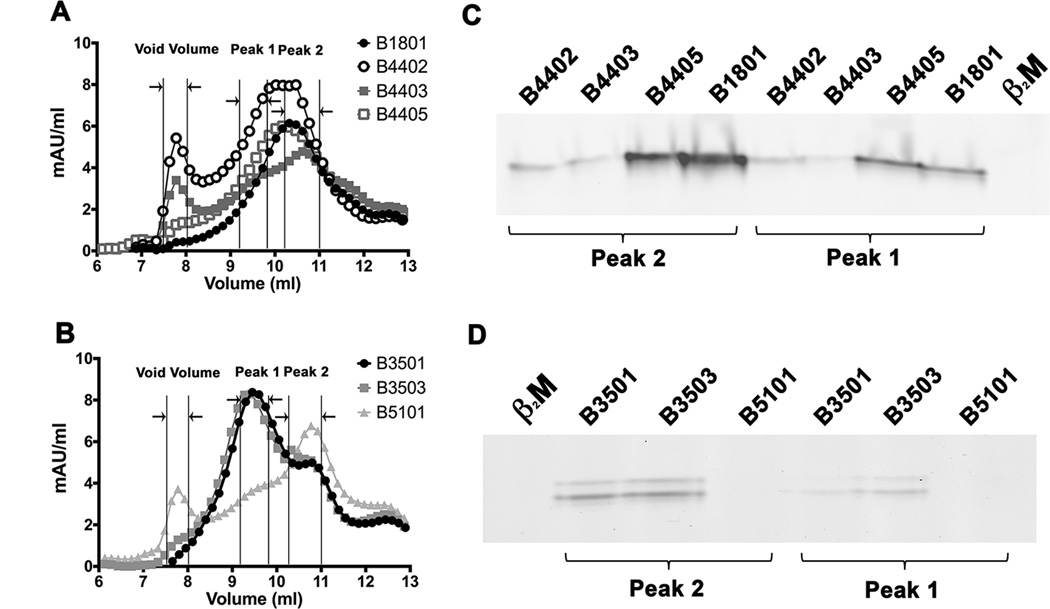
Figure 3. Higher assembly competence of soluble refolded tapasin-independent HLA-B allotypes.
A soluble form of the indicated HLA class I heavy chains (2 µM) was refolded with β2m (4 µM) overnight at 4 °C in the presence of TEV. Following refolding, the soluble fractions were analyzed by gel filtration chromatography using a Superdex 75 10/300 GL column. Representative gel filtration analyses of A) B1801, B4402, B4403 and B4405 (B44 supertype) and B) B3501, B3503 and B5101 (B7 supertype) are shown. The vertical lines show peak position ranges of the gel filtration column void volume (left), Peak 1 (middle) and Peak 2 (right). C and D) Peak 1 and Peak 2 fractions from A and B were assessed for their peptide binding competence. Peak 1 and Peak 2 fractions were normalized for protein concentration (to 200 nM (Peak 1) or 400 nM (peak 2) for B44 supertypes, and 20 nM (peaks 1 and 2) for B7 supertypes) and incubated with a 10-fold excess of refolded β2m and FITC labeled peptide (peptide EEFGKFITCAFSF for B44 supertypes and peptide IPLKFITCEEAEL for B7 supertypes). Peptide bound heterodimers were separated by native gel electrophoresis and visualized by fluorescence scanning. Both Peak 1 and Peak 2 fractions are competent for peptide binding. Representative data of four independent measurements are shown.