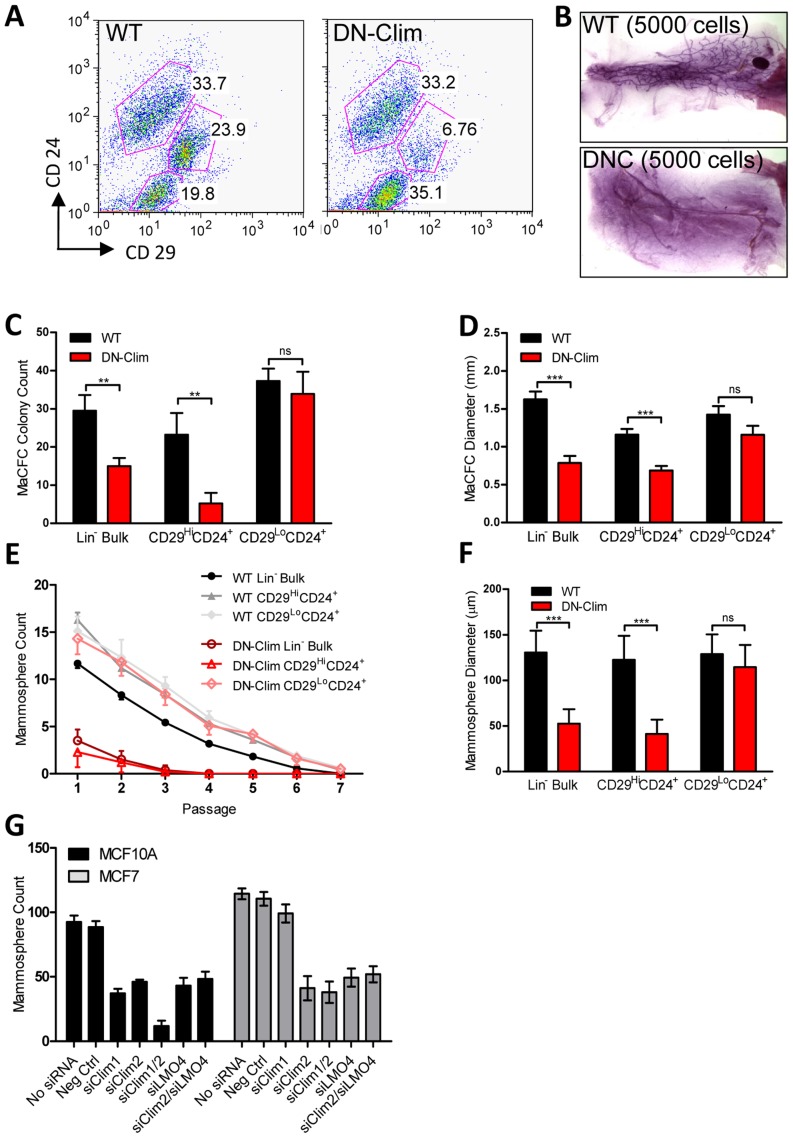
Figure 4. Clims maintain basal mammary epithelial stem cells.
(A) Flow cytometry analysis of Lin− MECs with CD29 and CD24 markers reveals decreased CD29HiCD24+ basal epithelial cell population. (B) DN-Clim mammary glands are absent of MRUs as demonstrated in representative whole mounts from transplants of CD29HiCD24+ BSC-enriched population. See Table 1 for results from limiting dilution analysis. (C) DN-Clim basal cells, and not luminal cells, maintain fewer colony forming units determined by colony-forming cell assays with Lin− bulk and sorted primary mammary epithelial cells. (D) Reduced growth rates in colonies that form from DN-Clim basal cells determined by quantification of colony size for the corresponding MaCFC assays described in (C). (E) DN-Clim basal cells, and not luminal cells, maintain fewer mammosphere forming units determined by mammosphere assays with Lin− bulk and sorted primary mammary epithelial cells. (F) Reduced growth rates in spheres that form from DN-Clim basal cells determined by quantification of mammosphere diameter for the first passage of the mammosphere assays described in (E). (G) Clim1, Clim2 and the Clim interaction factor LMO4 are essential for maintaining stem-like features of MCF10A cells, as determined by mammosphere assays with transient siRNA knockdown of Clim1, Clim2, and LMO4. In MCF7 cells, only Clim2 and LMO4 maintain stem-like features. Data represent mean ± SEM from at least three mice (C–F) or at least three experiments (G). ** p-value<0.01; *** p-value<0.001, ns: not significant.