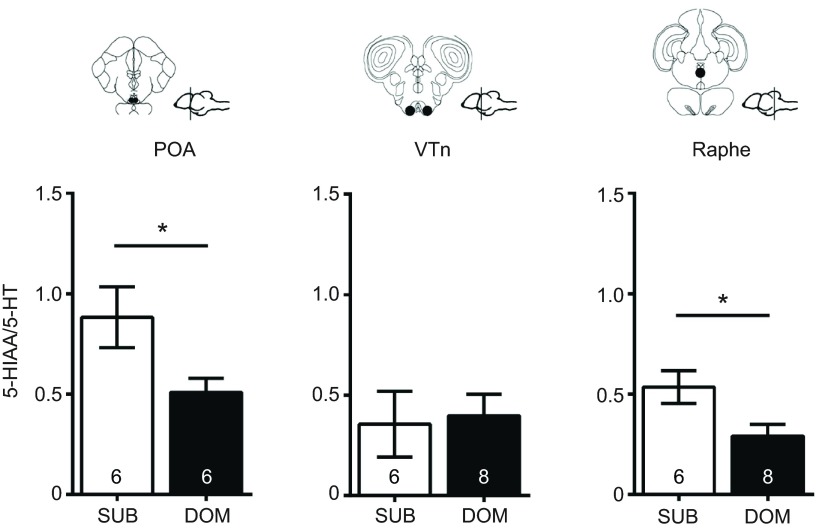
Fig. 4.
Serotonergic turnover in A. burtoni varies by social status in a brain region-specific manner. Levels of 5-HT and its catabolite 5-hydroxyidoleacetic acid (5-HIAA) were measured in microdissected tissue from the preoptic area (POA), ventral tuberal nucleus (VTn) and raphe of subordinate and dominant males. Using the 5-HIAA/5-HT ratio as a proxy for serotonergic turnover, we found subordinate males had a higher turnover in the POA and raphe, but not the VTn, compared with dominant males. Representative coronal sections and sagittal brain diagrams illustrate the location of the quantified regions (circled area) for each brain nucleus. Numbers inside bars indicate group size and error bars indicate ±s.e.m. Asterisks indicate a statistical difference between social groups at P<0.05, Mann–Whitney U-tests.