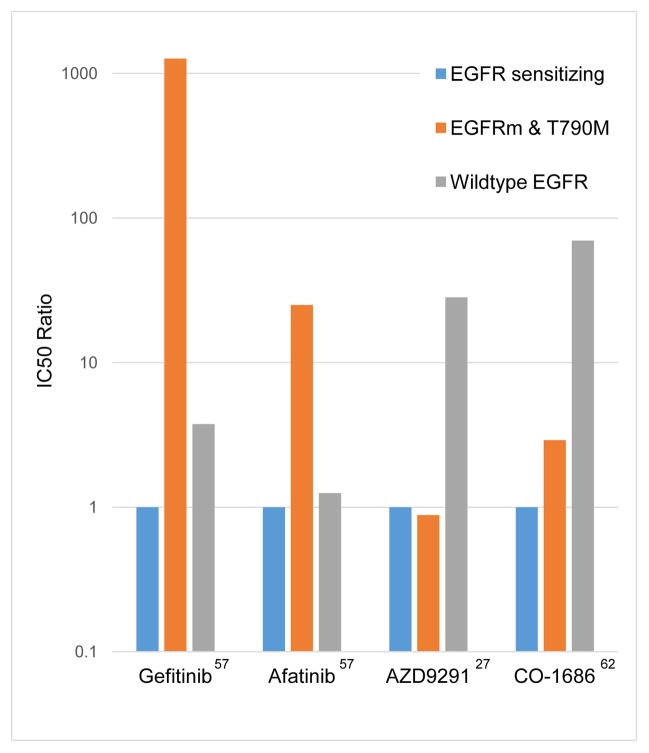
Figure 3.
Relative potency of different EGFR kinase inhibitors against different EGFR genotypes in vitro. The Y-axis represents the relative IC50 normalized to the IC50 against EGFR sensitizing mutations (L858R or exon 19 deletion).27,57,62 Second-generation EGFR TKIs like afatinib are more potent against T790M than gefitinib, but dosing in the clinic is limited by wildtype inhibition (and toxicity) at a relatively lower dose. Third-generation EGFR TKIs like CO-1686 and AZD9291 selectively inhibit EGFR T790M well below the dose at which wildtype EGFR is inhibited and have the potential to yield reduced toxicity as a result.