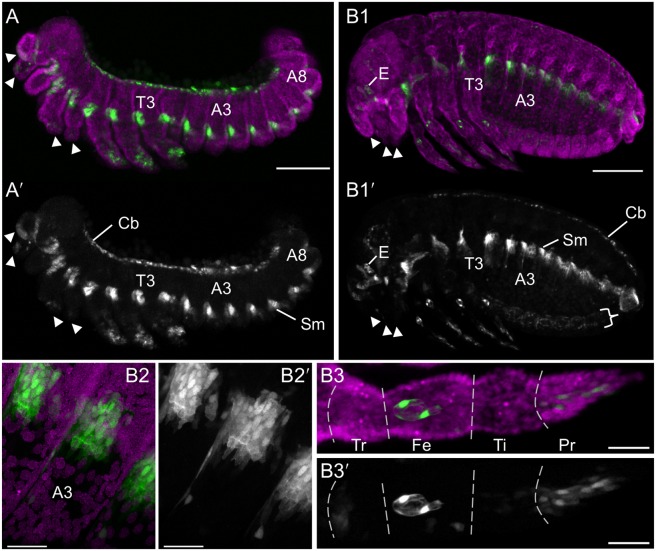
Figure 5. Expression in the line G04609: muscle and leg sensory cell anatomical details.
For the retracted germband (A) and post-dorsal closure (B) stages, representative embryos are shown with G04609-mesodermal×G12424-serosal heterozygote EGFP expression (green; white in single-channel images) and a nuclear counterstain (magenta). The serosa and dorsal yolk have been removed in image A. G04609 muscle EGFP persists in lateral segmental blocks (A,B1,B2). Meanwhile, expression in the appendages is dynamic. The distal tips of the labral, antennal, maxillary, and labial segments (but not the mandibulary segment) initially express EGFP, but this is subsequently lost (compare arrowheads in A and B1). In the legs, distal expression is initially broad (A) and later refines to a subset of putative sensory structures (B1,B3): a small, anterior-proximal patch in the trochanter, a circular structure and single anterior-distal cell within the femur, and cells throughout the pretarsus (shown for the T2 leg). The expression in the trochanter and single labeled cell in the femur are superficial and likely represent sensory cells within the ventral epidermis, such as campaniform sensillae [55]. The circular structure lies in the center of the femur’s diameter and is anatomically consistent with identification as the chordotonal organ [56]. The expression in the pretarsus is distally superficial but innervates the leg more proximally and also likely represents sensory structures. Lastly, EGFP expression also occurs weakly throughout the ventral nerve cord at post-dorsal closure stages, due to the 3xP3 enhancer in the transposon (B1′: curly bracket). All views are maximum intensity projections in lateral aspect, with anterior left or proximal left (B3 only). Abbreviations: A(x), abdominal segment (x); Cb, cardioblasts; E, eye; Fe, femur; Pr, pretarsus; Sm, segmental muscle blocks; T(x), thoracic segment (x); Ti, tibiotarsus; Tr, trochanter. Scale bars are 100 µm (A,B1) and 20 µm (B2,B3).