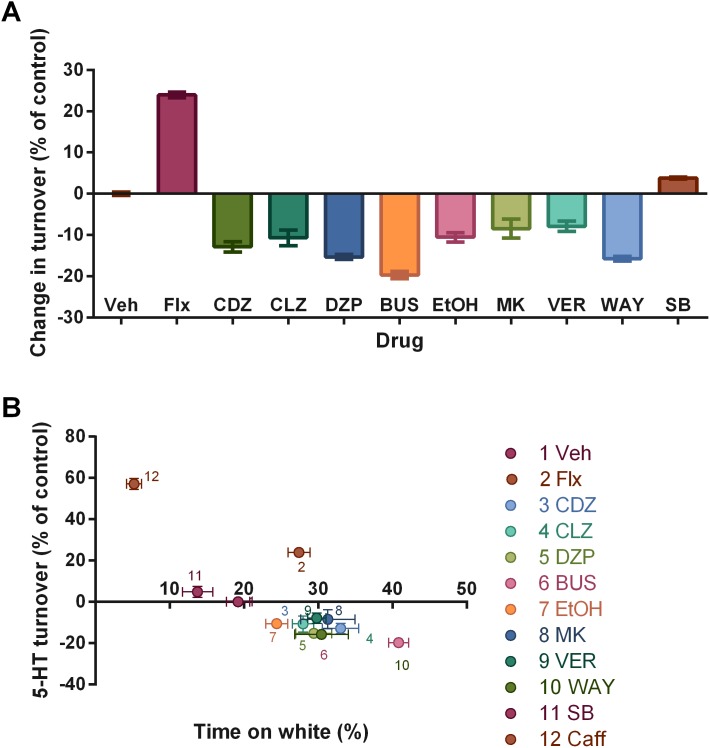
Figure 4. Drugs which cluster on the 'anxiolytic' group decrease 5-HT turnover in the brain.
(A) Turnover rates, as measured by 5-HIAA:5-HT ratios, normalized to the values of vehicle-treated animals, for the following drugs: fluoxetine (FLX; chronic treatment with 10 mg/kg); chlordiazepoxide (CDZ; 0.02 mg/kg); clonazepam (CLZ; 0.05 mg/kg); diazepam (DZP; 1.25 mg/kg); buspirone (BUS; 50 mg/kg); ethanol (EtOH, 2.5%); dizocilpine (MK; 0.005 mg/kg); verapamil (VER; 5 mg/kg); WAY 100,635 (WAY; 0.03 mg/kg); and SB 224,289 (SB; 2.5 mg/kg). Asterisks mark statistically significant differences in relation to vehicle-treated animals (F10, 43 = 45.99, p<0.0001, one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's Multiple Comparison test). Bars represent mean (B) Correlation between turnover rates (Y-axis) and time spent in the white compartment (X-axis) for vehicle- and drug-treated animals (n = 4 for each point). Points represent means and error bars represent standard errors. A negative correlation is found between the decrease in serotonin turnover and the increase in time on white produced by a drug (r2 = 0.5688, p = 0.0073).