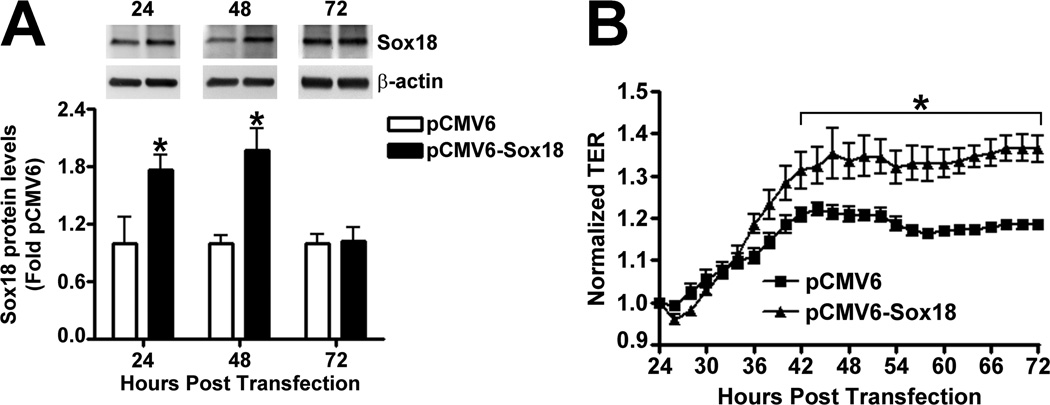
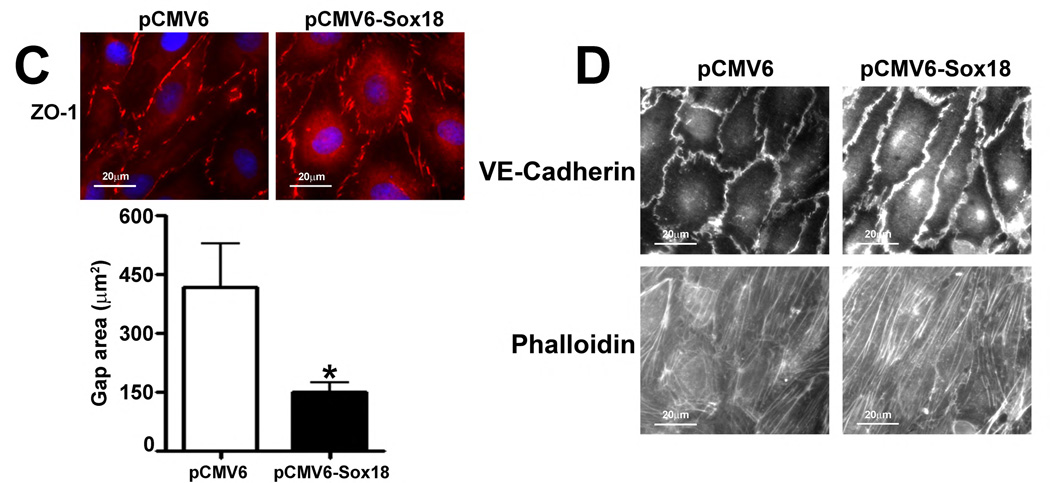
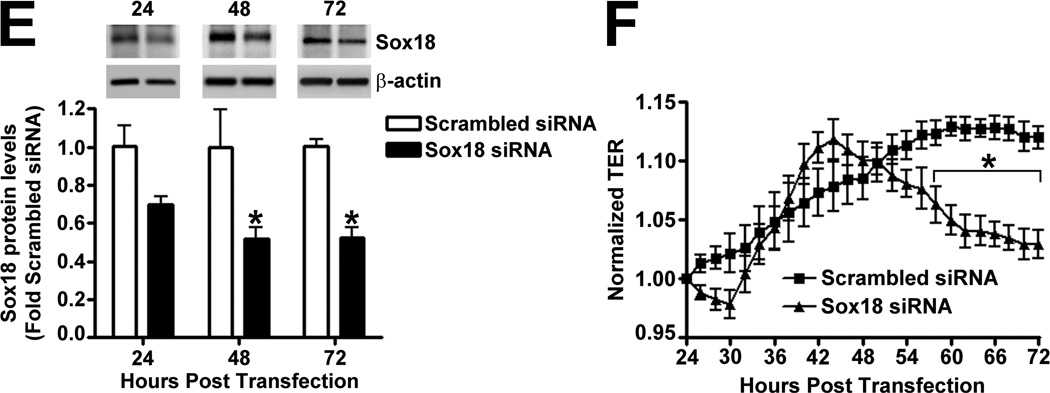
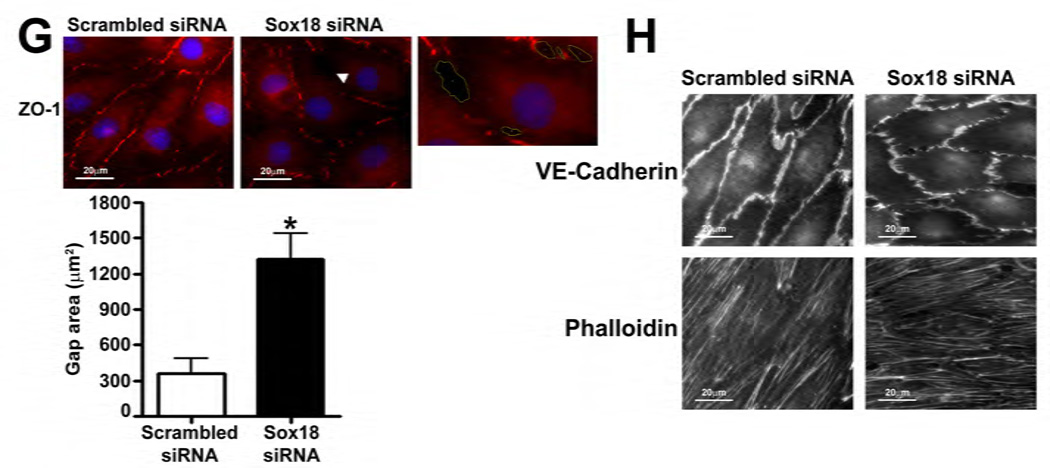
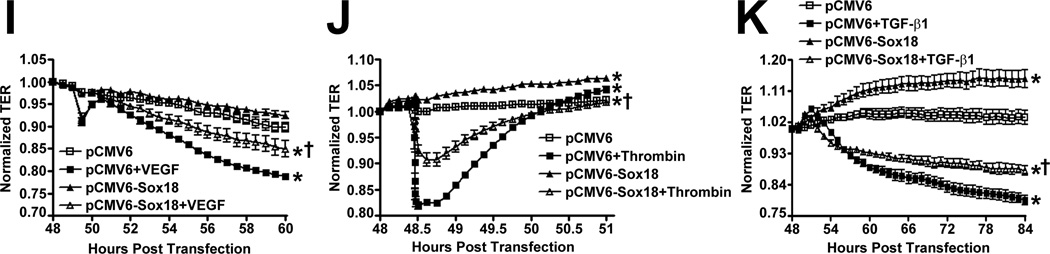
Fig. 2. Sox18 protects endothelial barrier function in pulmonary artery endothelial cells.
PAEC were transfected with either pCMV6 or pCMV6-Sox18 for 24–72 h. Immunoblot analysis indicated an increase in Sox18 protein levels after 24 h and 48 h of transfection (A). PAEC monolayers grown on gold microelectrodes (B) or glass coverslips (C & D) were transfected with either pCMV6 or pCMV6-Sox18. After 42 h post transfection, the normalized trans-endothelial resistance (TER) was significantly increased in pCMV6-Sox18 transfected PAEC (B). In addition, immunofluorescent staining of tight junctions was performed using an Alexa Fluor 594 conjugated Zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1) antibody; the nuclei were stained with DAPI. After 48 h, the over-expression of pCMV6-Sox18 decreased inter-cellular gap formation (C). Immunofluorescent analysis of adherens junctions indicated increased VE-cadherin staining but no changes in stress fiber formation (D). In contrast, the siRNA mediated knockdown of Sox18 decreased Sox18 protein levels after 48 and 72 h (E) and the TER after 58 h of transfection (F). Additionally, the immunofluorescent staining of inter-cellular tight junctions demonstrated that, after 48 h, the Sox18 depleted monolayers displayed enhanced gap formation (G). Similarly, these cells displayed a loss of junctional VE-cadherin staining but no alterations in stress fiber formation (H). Further, when the PAEC transfected with pCMV6 were exposed to VEGF (500ng/ml) (I), thrombin (100nM) (J), or TGF-β1 (10ng/µl) (K) for the indicated amount of time, there was a gradual decrease in TER. However, the transfection of cells with pCMV6-Sox18 attenuated the decline in TER induced by VEGF (I), thrombin (J), and TGF-β1 (K). Values are mean ± SEM, n=3–6. *p<0.05 vs. pCMV6 (AC, I–K) or Scrambled siRNA (E–G); † P<0.05 vs. pCMV6+VEGF (I), pCMV6+Thrombin (J), pCMV6+TGF-β1 (K).