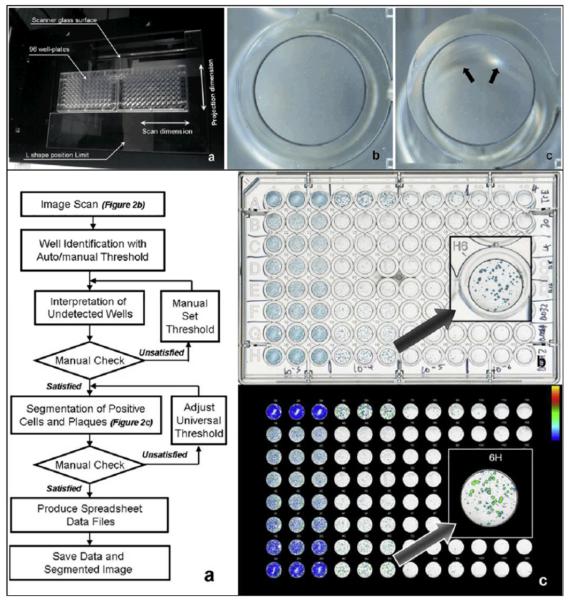
Figure 4.
A CCD based flatbed scanner used to evaluate a plaque assay measuring the infectivity and replication inhibition of various influenza virus strains in the presence of oseltamivir carboxylate. (Top) (a) Two 96-well plates are placed in the middle of the CCD based scanner to minimize the out-of-focus artifacts created by the wells placed far from the optical axis of the scanner lens. The artifact is depicted in (c), and can be compared to an image of a well taken from the middle of the plate shown in (b). (Bottom) (a) Image post processing algorithm for automatic evaluation of the scanned images. (b) Scanned image of the 96 well plate containing modified Madin-Darby canine kidney cells in triple columns infected with (from left to right) 103–106 of influenza virus A/Trieste/25/2007 and treated with 5 fold dilutions of oseltamivir carboxylate (20–0.0013nM,rows B to H) and row A as cell control with no oseltamivir carboxylate. (c) Positive population shown in a pseudo-colored image. Reprinted from Journal of Virological Methods, 179, Kate Sullivan, Johannes Kloess, Chen Qian, Donald Bell, Alan Hay, Yi Pu Lin, Yan Gu, “High throughput virus plaque quantitation using a flatbed scanner”, 81–89, Copyright (2012), with permission from Elsevier30.