Figure 1.
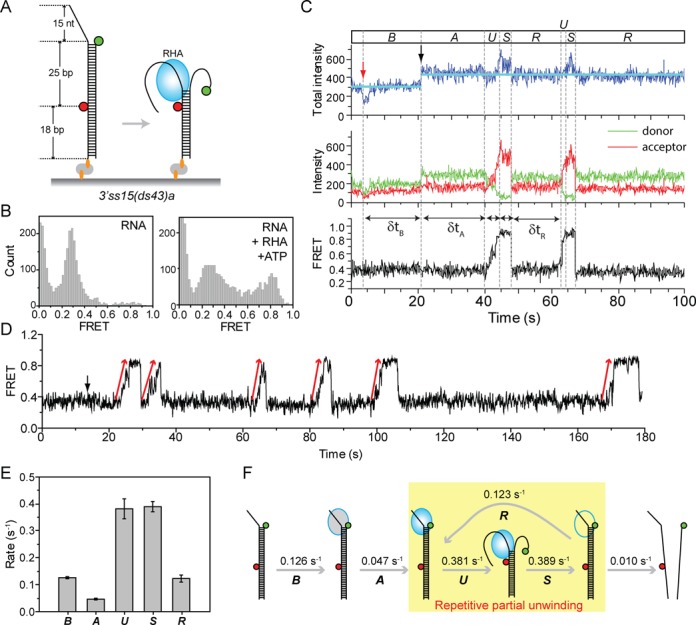
RHA unwinds dsRNA stepwise in a repetitive manner. (A) A diagram of an immobilized RNA substrate used for unwinding. (B) FRET histograms showing the RNA unwinding of RHA in the presence of ATP. (C) A representative smFRET trace showing the real-time RNA unwinding process of RHA, which can be dissected into five distinct kinetic substeps (B for binding, A for activation, U for unwinding, S for stalling and R for re-activation). The red arrow indicates the moment of adding RHA and ATP. The black arrow indicates the initial RHA binding to RNA. (D) A representative smFRET trace showing multiple rounds of unwinding upon binding of a single RHA to an RNA molecule. (E) The kinetic rate of each substep determined in the presence of 40 nM RHA and 1 mM ATP at room temperature. All error bars denote SEM from at least three independent experiments. (F) Proposed model of unwinding mechanism of RHA.
