Figure 2.
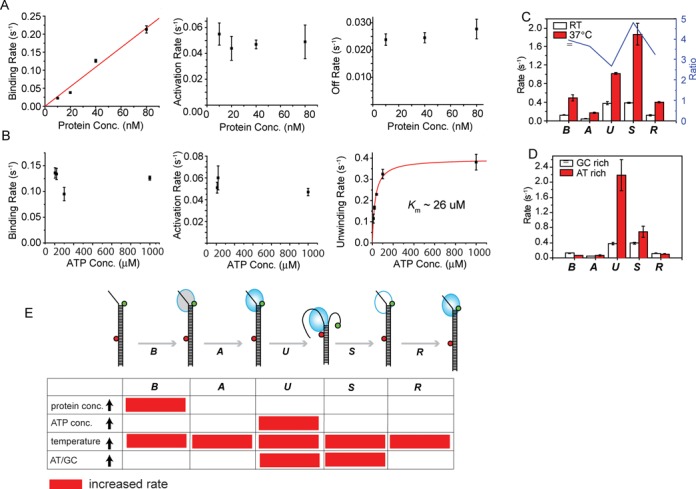
Kinetic characterization of each substep in the RNA unwinding process of RHA by varying RHA or ATP concentrations, temperature or duplex sequence composition. (A) The rate of RHA binding to dsRNA increases linearly with the increasing RHA concentration, giving an association constant of 2.61 μM−1 s −1 (left). RHA concentration does not affect the activation of RHA (middle) and the off rate of RHA (right). (B) ATP concentration does not change binding (left) and activation rate (middle), yet it modulates unwinding rate (right). The Km is ∼26 μM from a Michaelis–Menten plot (right). (C) RHA unwinding at 37°C displaying accelerated rates for all the substeps in the unwinding process. The ratio of the kinetic rate at 37°C to the one at RT is displayed as a blue line with a right y-axis. (D) AT-rich RNA sequence gives rise to a dramatic enhancement of the unwinding substep, a slight increase in the stalling rate, but does not significantly affect other substeps. All error bars denote SEM from at least three independent experiments.
