Figure 4.
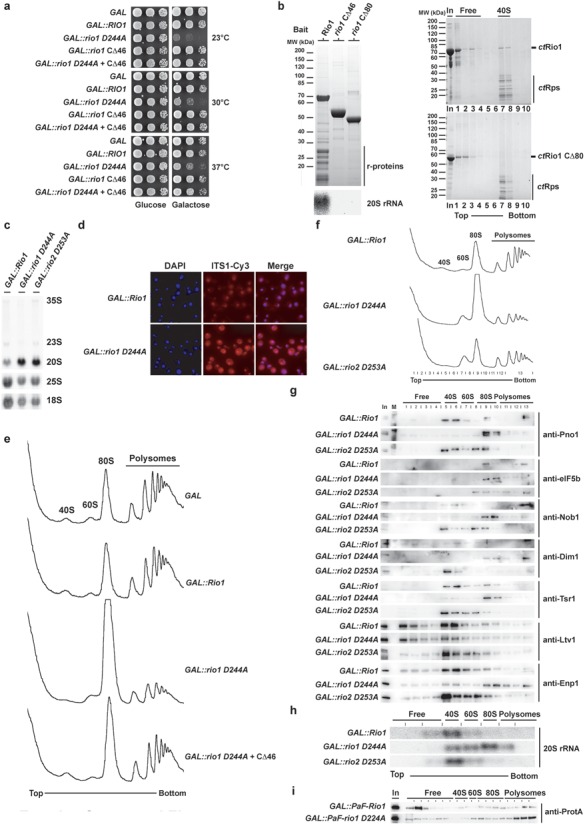
Rio1 dominant negative mutant shows a translation-like initiation defect and delocalization of late ribosome biogenesis factors. (a) Overexpression of rio1 D244A induces a dominant negative growth defect. Serial dilutions of wild-type cells carrying the multi-copy GAL empty vector or the same plasmid with indicated galactose-inducible Rio1 alleles were spotted on SDC-Ura (repressed) and SGC-Ura (induced) plates for 2 or 3 days at 30°C–37°C and 23°C, respectively. (b) Rio1 C-terminal part is required for (pre-) 40S binding. Wild-type yeast cells (BY4741-Euroscarf) transformed with a plasmid carrying the indicated bait protein fused with N-terminal ProtA-TEV-Flag under the control of the ADH1 promoter were grown in SDC-Leu up to OD600 = 1.5. Indicated bait proteins were purified by standard tandem affinity purification (see the Materials and Methods section). Co-immunoprecipitated proteins from Flag eluates were precipitated by addition of TCA and resolved on a 4–12% Nupage gel (Invitrogen) and visualized by coomassie staining. RNA was extracted by hot-phenol extraction and resolved on a 1.2% agarose formaldehyde/MOPS (3-(N-morpholino)propanesulfonic acid) gel, and transferred to a positively charged nylon membrane. For northern blot analysis membrane was hybridized with the indicated probe (see the Materials and Methods section) and exposed to a Phosphorimager screen. For in vitro binding (right panel) purified ct40S (10 pmol) and the indicated ctRio1 constructs (100 pmol) were mixed in binding buffer and incubated at Room Temperature (RT) for 10 min prior to loading on sucrose gradient. Fractions were collected, proteins were TCA precipitated, resolved by SDS-PAGE and visualized by coomassie staining. (c–d) Overexpression of catalytically inactive Rio1 induces cytoplasmic 20S rRNA processing defect. Northern blot analysis of steady-state (pre-) rRNA species using probes complementary to the ITS1, 18S and 25S mature region of the rRNA and steady-state subcellular localization of ITS1 containing rRNA species was monitored by FISH using a Cy3-conjugated probe complementary to the ITS1 region of the rRNA on yeast cells after 6 h induction of the dominant negative phenotype (see the Materials and Methods section). (e) Overexpression of rio1 D244A induces a translation initiation-like defect. Polysomes profile analysis obtained from whole cell lysates from yeast cells overexpressing the indicated constructs for 6 h is shown. The A254nm profiles of the derived sucrose gradients fractions are depicted. (f) Same as in (e) except that the indicated fractions were collected, TCA precipitated and analyzed by western blotting [shown in (g)]. (g) Overexpression of rio1 D244A induces relocalization of several late 40S biogenesis factors in the 80S fraction. TCA-precipitated fractions obtained from the sucrose gradient shown in (e) were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and western blotting using the indicated antibody (see the Materials and Methods section). (h) Overexpression of rio1 D244A induces relocalization of 20S rRNA in the 80S fraction. Similar to (g), RNA from sucrose gradient fractions was extracted and analyzed by northern using a probe complementary to the ITS1 region. (i) Overexpressed rio1 D244A mostly localized in 80S and polysomes fractions. Polysomes profile analysis obtained from whole cell lysates from yeast cells overexpressing Gal::ProtA-TEV-Flag-Rio1 or rio1 D244A was induced for 6 h prior to cycloheximide treatment. The indicated fractions were collected, TCA precipitated and analyzed by western blotting.
