Figure 7.
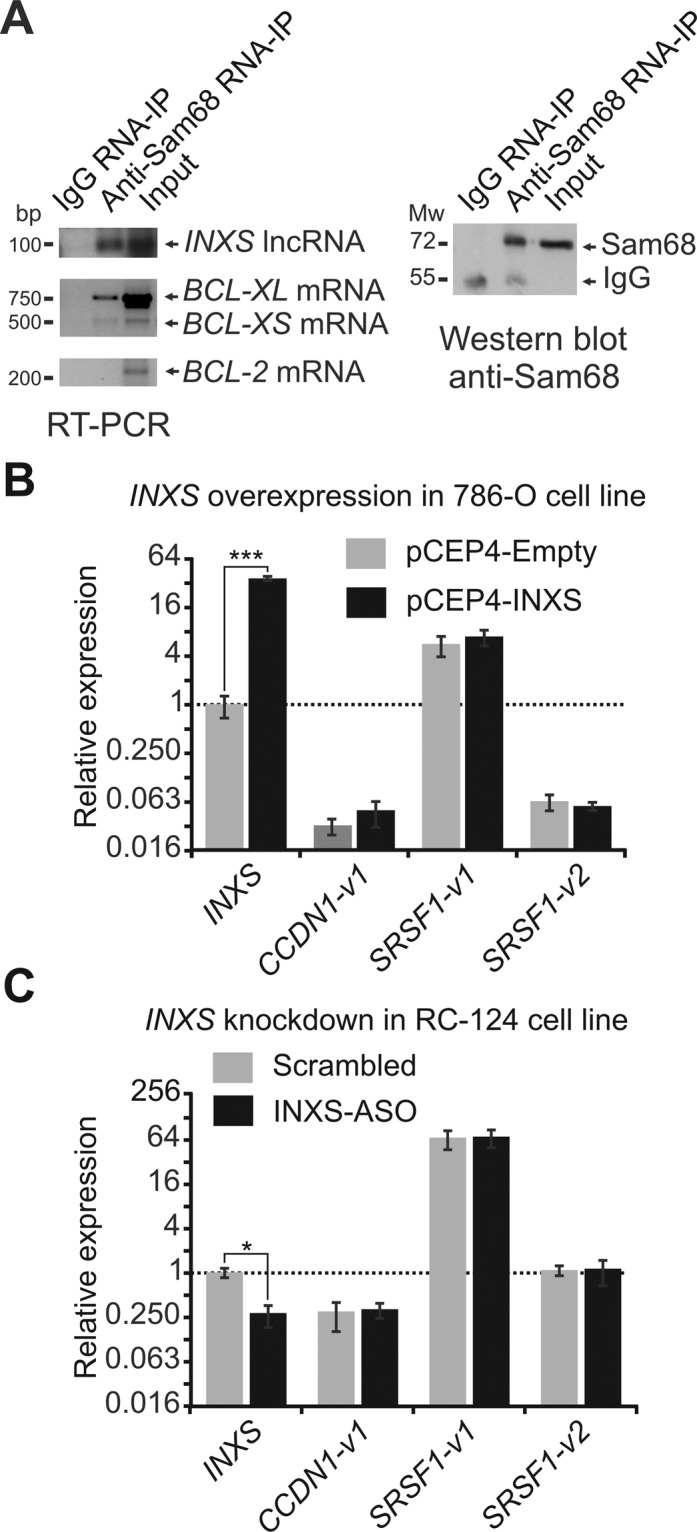
INXS interacts with the Sam68 splicing-modulator complex. (A) Native RIP (RNA-binding protein immunoprecipitation) assay with anti-Sam68 antibody was performed, followed by RT-PCR with primers for the indicated genes. A negative control, from RNA-IP with immunoglobulin G (IgG) was included. For INXS lncRNA, a strand-specific primer was used for RT. For the positive controls (BCL-XL and BCL-XS mRNAs) and the negative control (BCL-2 mRNA), oligo-dT primer was used for RT. The protein fraction from the native RIP assay with anti-Sam68 antibody was analyzed by western blot, which was developed with the same antibody. A negative control sample, from RIP with IgG, was included. (B) INXS overexpression was performed in the 786-O kidney tumor cell line with 3 μg of INXS-expressing plasmid for 24 h and the alternative splicing isoforms of two Sam68 target mRNAs that have been identified in the literature, namely, CCDN1-v1 and SRSF1-v1 and -v2, were measured by RT-qPCR. (C) INXS knockdown was performed in the RC-124 kidney non-tumor cell line as in Figure 2, and the levels of CCDN1-v1 and SRSF1-v1 and -v2 were measured by RT-qPCR. The data are the mean ± SD of three independent experiments.
