Figure 2.
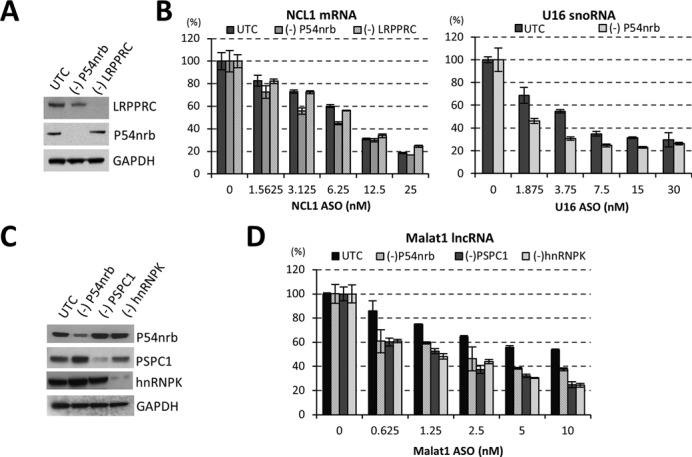
Reduction of paraspeckle proteins increases the activity of RNase H1-based ASOs. (A) siRNA-mediated reduction of P54nrb and LRPPRC proteins, as determined by western analysis. UTC, mock treated control cells. GAPDH served as a loading control. (B) Reduction of P54nrb, but not LRPPRC, increased the activity of ASO-mediated cleavage of NCL1 mRNA (left panel) or U16 snoRNA (right panel), as determined by qRT-PCR analysis. (C) siRNA-mediated reduction of paraspeckle proteins P54nrb, PSPC1 and hnRNPK, as determined by western analysis. GAPDH served as a loading control. (D) Reduction of other paraspeckle proteins can also increase ASO activity, as exemplified with an ASO targeting Malat1 lncRNA, as determined by qRT-PCR. The error bars represent standard deviation from three parallel experiments.
