Figure 2.
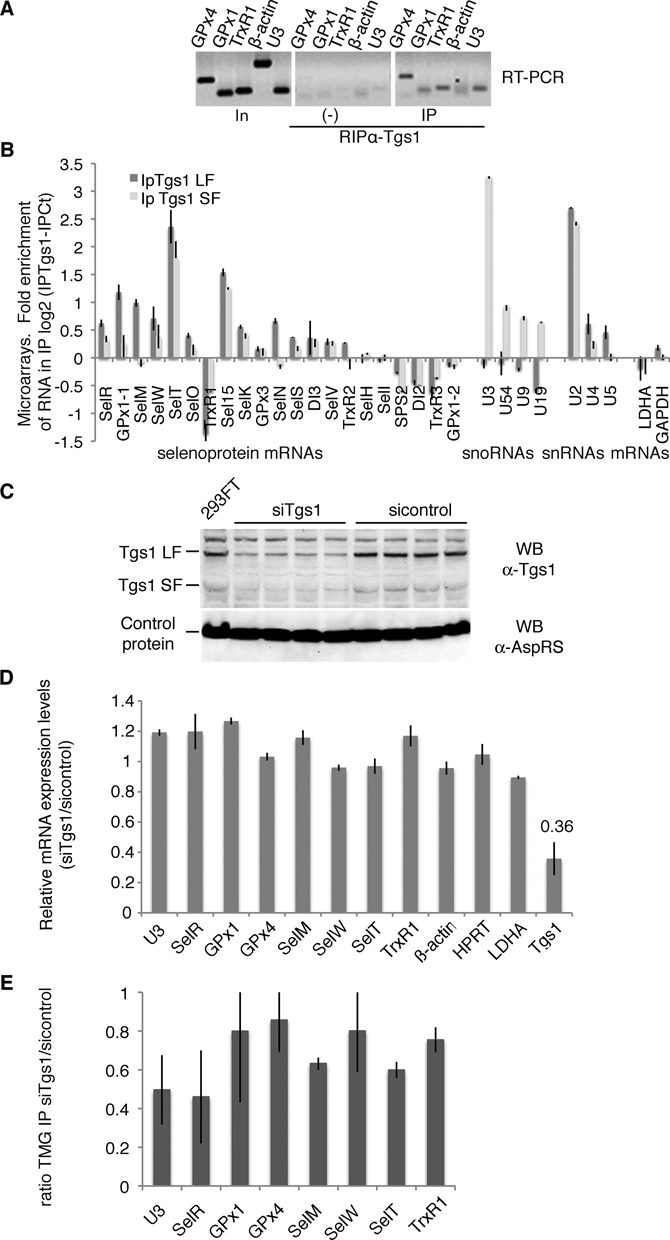
Tgs1 is involved in selenoprotein mRNA cap hypermethylation. (A) Tgs1 interacts with selenoprotein mRNAs in vivo. HEK293FT cells transfected with SBP2 were immunoprecipitated using anti-Tgs1 antibodies. Bound RNAs were detected by RT-PCR. In: input 15%; (−) no antibodies; U3: positive control; β-actin: negative control. (B) Tgs1 LF and SF associate with selenoprotein mRNAs. Isogenic HeLa cells stably expressing 3XFlag tagged Tgs1 LF and SF were used for anti-FLAG IPs, the RNA content was analyzed on microarrays. The control was the parental cell line that did not express any tagged protein. The graph represents the fold RNA enrichment in the IP in a log2 scale. Dark bars: Tgs1 LF IP; gray bars: Tgs1 SF IP. Data of all the expressed selenoprotein mRNAs are represented followed by examples of snoRNAs (U3 to U19), snRNAs (U2, U4, U5) and housekeeping mRNAs (LDHA and GAPDH). GPx1-1 and GPx1-2 are splice variants of GPx1. (C) Tgs1 inactivation by siRNA. Tgs1 mRNA was decreased to 36% which resulted in 35% of residual Tgs1 protein. Western blot detection of Tgs1 was performed using anti-Tgs1 antibodies; anti-AspRS antibodies were used as a control. siRNAs directed against firefly luciferase were used as controls (sicontrol). (D) siTgs1 did not have any effect on the steady state level of selenoprotein mRNAs. qRT-PCR was used to determine relative expression levels by the ΔΔCt method. (E) siTgs1 reduces hypermethylation efficiency. RNA-IP using anti-TMG serum was performed as described in Figure 1 under siTgs1 and sicontrol conditions. IP ratios between siTgs1 and sicontrol are represented by the histogram and deduced from Supplementary Figure S2. Error bars represent standard deviation of an average of three independent experiments.
