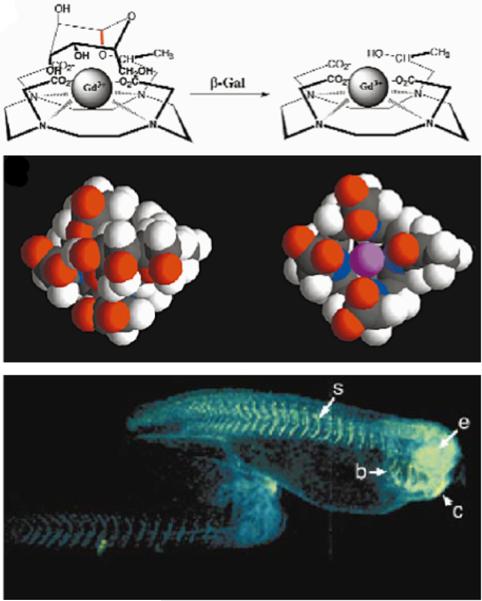
Figure 1.
Detecting enzyme activities through changes in T1 relaxation caused by alterations in water accessibility. Top panel: The cleavage of a galactopyranosyl ring of the T1 contrast agent, EgadMe, causes the inner sphere coordination site of the Gd3+ ion to become more accessible to water. Middle panel: A space-filling molecular model illustrates the increased accessibility of the Gd3+ ion (magenta) upon cleavage. Bottom Panel: Two living X. laevis embryos were injected with EgadMe, and the embryo shown on the right was also injected with β-galactosidase mRNA. The pseudocolor rendering of MR images shows that the signal strength is 45–65% greater in the embryo containing β-galactosidase mRNA, demonstrating the detection of β-galactosidase activity. Labeled anatomy: e, eye; c, cement gland; s, somite; b, brachial arches. Reproduced with permission from (22).