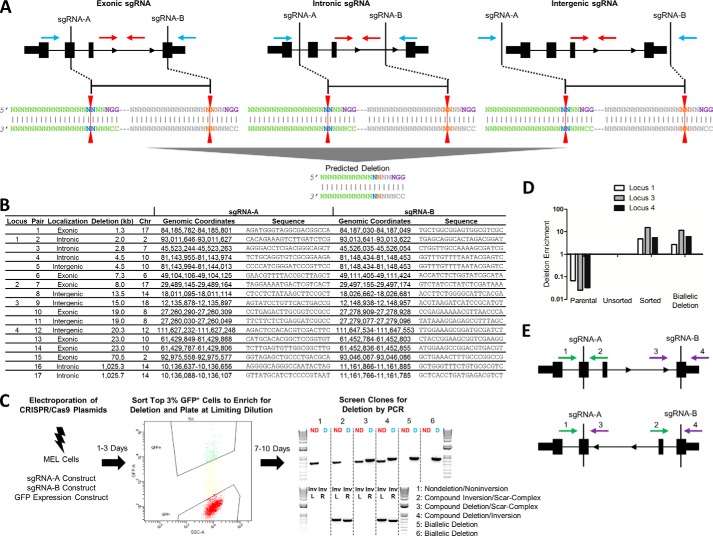
FIGURE 1.
Schema for CRISPR/Cas9-mediated genomic deletion. A, exonic, intronic, and intergenic sgRNA deletion strategies. The sgRNA sites are shown in relation to an idealized gene. The PAM sequence (purple) is shown on the top strand for simplicity, but PAMs on both the top (Watson) and bottom (Crick) strands were used in different combinations. The red line indicates the predicted Cas9 cleavage between positions 17 and 18. The blue arrows indicate the position of PCR primers for deletion band amplification, and the red arrows indicate the position of PCR primers for nondeletion band amplification. B, sgRNA localization (exonic/intronic/intergenic), deletion size, chromosome, genomic coordinates (mm10), and sequence for each sgRNA pair. Loci 1–4 used for further sequence analysis are indicated. C, CRISPR/Cas9-mediated genomic deletion strategy for MEL cells. 2 × 106 cells were electroporated with 5 μg of each sgRNA construct and 0.5 μg of a GFP expression construct. The top 3% of GFP+ cells were sorted 1–3 days post-electroporation and plated at limiting dilution. 7–10 days after plating, gDNA was extracted, and clones were screened for deletion by PCR. A representative screening agarose gel shows the detection of two nondeletion clones, two monoallelic deletion clones, and two biallelic deletion clones. The red ND refers to the nondeletion amplicon as schematized in A, and the blue D refers to the deletion amplicon as schematized in A. Upon inversion analysis, clones were further classified as nondeletion/noninversion, compound inversion/scar-complex, compound deletion/scar-complex, and compound deletion/inversion. The distinction between scar and complex was established by the presence or absence of PCR amplification flanking both sgRNA target recognition sites. Inv refers to inversion amplicons flanking left and right sgRNA recognition sites (L and R, respectively). D, gDNA was extracted from cells prior to (unsorted) and after sorting the top 3% of GFP+ cells (sorted). Deletion enrichment was calculated by RT-quantitative PCR, and data were normalized to the unsorted cells using the 2−ΔΔCt method. A biallelic deletion clone for each locus was used as a positive control and nonedited parental gDNA as a negative control. E, primers flanking the sgRNA recognition sites (shown in green and purple) were used to amplify 500–700-bp regions around each sgRNA site on nondeletion/noninversion alleles (primers 1/2 and 3/4, top panel). Inversion PCR utilized primer pairs (primers 1/3 and 2/4, respectively; bottom panel) in which both primers were in the same orientation, one inside and one outside the intended deletion.