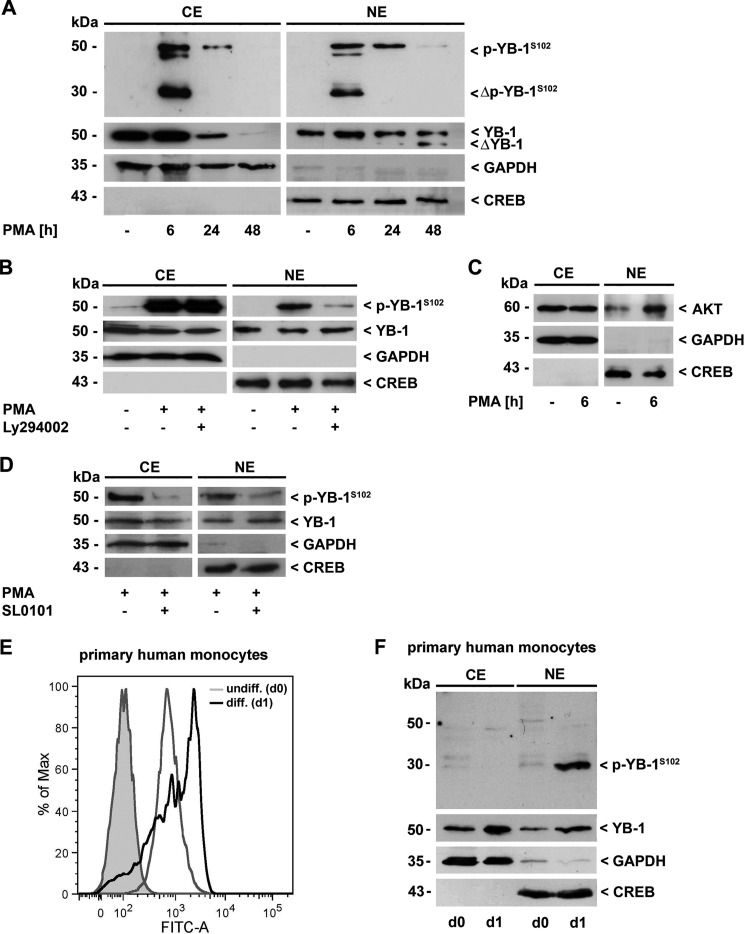
FIGURE 1.
YB-1 is transiently phosphorylated at Ser-102 in the course of monocyte differentiation. A, cytoplasmic (CE) and nuclear proteins (NE) of THP-1 cells were analyzed for p-YB-1S102 and total YB-1 content by Western blot analysis. Fragmentation and transient phosphorylation of YB-1 occurred in the course of PMA-induced monocyte differentiation (100 nm). B, YB-1 phosphorylation in the nucleus was effectively prevented by inhibition of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway by Ly294002 (10 μm). C, following PMA challenge (6 h), an enhanced presence of Akt in the nucleus was observed. D, inhibition of RSK by SL0101 resulted in reduced p-YB-1S102 content in both cytoplasm and nucleus. E, differentiation process of human primary monocytes was monitored by enhanced ICAM-1/CD54 expression as a macrophage marker molecule through FACS analysis. F, enhanced p-YB-1S102 content and fragmentation was observed in CE/NE of primary human monocytes (pooled from three healthy individuals for each experiment) during serum-induced differentiation. Successful separation of cell compartments and equal protein loading were ensured by determining GAPDH and CREB levels. The immunoblot is a representative from three independent experiments.