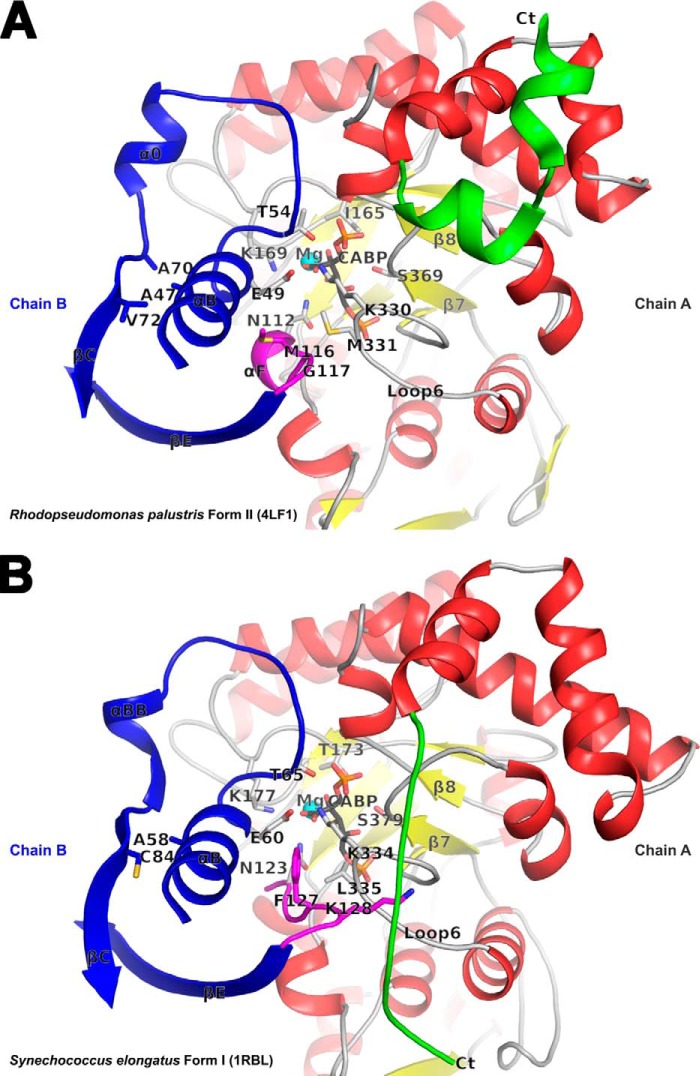
FIGURE 6.
Comparison of the active site regions in R. palustris form II (A) and Synechococcus form I (B) Rubiscos with contributing residues from two subunits (chains A and B) in each structure. The carboxyl-terminal domains of chain A (in red, yellow, green, and gray) and selected secondary structure elements in chain B (in blue and magenta) comprise key regions that affect catalysis. The active site residues, CABP, and other residues of interest are shown in stick representation. The carboxyl terminus with dissimilar conformation among the two structures that was also targeted for analysis via the construction of chimeric enzymes is colored green in both. In the Synechococcus form I structure, Lys128 (magenta) is interlocked between the carboxyl terminus (Ct) and loop 6 via multiple van der Waals interactions; the equivalent residue is Gly117 in the R. palustris form II structure. The relative positions of the R. palustris Ile165, Met330, and Ala47 and the analogous residues in the Synechococcus structure are all shown in the context of other active site residues.