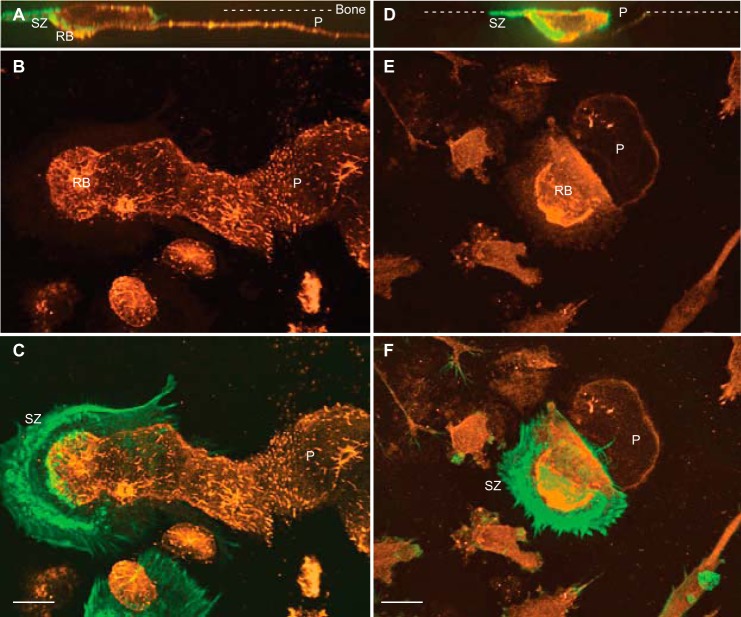
FIGURE 7.
Localization of C4-S and cathepsin K in human OCs during bone resorption. Multinucleated OCs were cultured on bone slices, fixed, and immunostained with either anti-C4-S or anti-CatK antibodies (orange) and then with phalloidin for F-actin (green). A, B, D, and E, confocal images of XZ sections (A and D), merged Z sections of C4-S and CatK stained OCs (B and E), respectively. C and F, overlaid images of C4-S or CatK and F-actin are shown. Active OCs form the sealing zone (SZ) on bone surface (dashed lines) and generate deep and long bone resorption pits (P). C4-S is weakly stained in the cytoplasm but strongly localized in the ruffled border (RB) and bone resorption pits (A–C). Total CatK is detected in the cytoplasm and resorption pits but highly accumulated in deep ruffled border (RB) of OCs (D–F). Bars, 12 μm.