Figure 2.
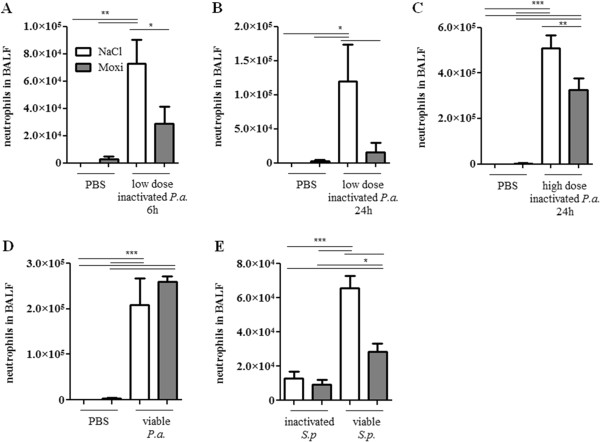
Moxifloxacin treatment results in a reduced influx of neutrophils into the lung during bacterial pneumonia. BAL fluids of moxifloxacin- and saline-treated mice were collected 6 or 24 h post intranasal infection with heat-inactivated P. aeruginosa(A/B/C), viable P. aeruginosa(D), and heat-inactivated or viable S. pneumoniae(E). Total numbers of neutrophils were determined. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. Bars indicate significant differences of *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001, (n ≥ 5 for each group).
