Extended Data Figure 7. Brca1 contributes quantitatively and qualitatively to HR at stalled replication forks.
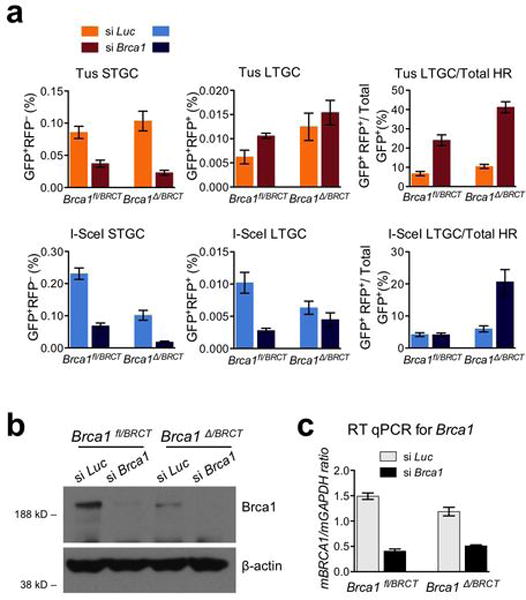
a, Frequencies of Tus-induced and I-SceI-induced HR in Brca1fl/BRCT and Brca1Δ/BRCT 6xTer/HR cells transiently co-transfected with Tus, or I-SceI and with either control Luciferase siRNA (si Luc) or Brca1 SMARTpool (si Brca1). Each column represents the mean of triplicate samples for each independent clone from seven independent experiments (i.e., n=7). Error bars: s.e.m. Tus-induced HR, Brca1fl/BRCT cells, t-test si Brca1 vs. si Luc: STGC: P= 0.0013; LTGC: P= 0.0206; LTGC/total HR: P= 0.0003; Brca1Δ/BRCT cells, si Brca1 vs. si Luc: STGC: P= 0.0016; LTGC: P= 0.4558; LTGC/total HR: P< 0.0001. I-SceI-induced HR, Brca1fl/BRCT cells, t-test si Brca1 vs. si Luc: STGC: P< 0.0001; LTGC: P= 0.0033; LTGC/total HR: P= 0.9214; Brca1Δ/BRCT cells, si Brca1 vs. si Luc: STGC: P= 0.0013; LTGC: P= 0.2348; LTGC/total HR: P= 0.0071. b, Brca1 protein levels and beta-actin loading control in Brca1fl/BRCT and Brca1Δ/Exon11 in siRNA-treated cells as shown. c, RT qPCR analysis of Brca1 mRNA in siRNA-treated cells as shown. (Source Data 6.)
