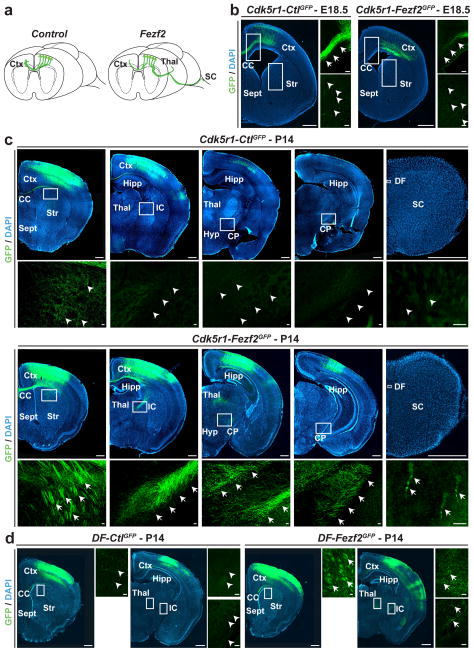
Figure 5. CPN can reprogram their axonal projections from callosal to corticofugal targets in response to Fezf2.
a, Graphic representation of changes in axonal connectivity by layer II/III CPN in response to Fezf2 versus control. b, GFP-positive CPN axons crossing the corpus callosum at E18.5 in Cdk5r-Fezf2eGFP and Cdk5r-CtleGFP-electroporated CPN. Callosal projections are greatly reduced in Cdk5r-Fezf2eGFP- versus Cdk5r-CtleGFP-electroporated CPN. c, At P14, GFP-positive axons are restricted to the corpus callosum in Cdk5r-CtleGFP-electroporated CPN. By contrast, axons of Cdk5r-Fezf2eGFP-electroporated CPN are also present in the internal capsule and extend caudally to the thalamus and the cerebral peduncle. A small number of GFP-positive axons are present in the dorsal funiculus of the spinal cord in Cdk5r-Fezf2eGFP- but not in control-electroporated animals. d, GFP-positive axons at P14 of DF-Fezf2eGFP- or DF-CtleGFP-electroporated CPN that received TAM postmitotically at E17.5. Callosal axons are restricted to the corpus callosum in DF-CtleGFP CPN while axons are also present within the internal capsule in DF-Fezf2eGFP CPN. CC, corpus callosum; CP, cerebral peduncle; Ctx, cortex; DF, dorsal funiculus; Hipp, hippocampus; Hyp, hypothalamus; IC, internal capsule; Str, striatum; Sept, septum; Thal, thalamus. Scale bars, 200 μm and 20 μm in high magnification panels.