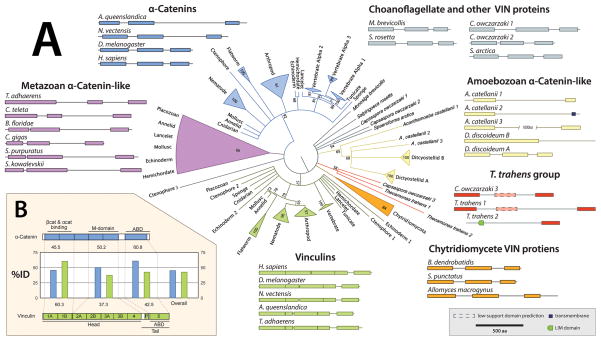
Figure 7. Evolutionary History of VIN Families.
(A) A maximum likelihood phylogeny of 96 VIN-containing proteins generated using RAxML (Stamatakis, 2006) with 1000 rapid bootstrap iterations and best-fit model parameters as determined by ProtTest3 (PROTGAMMALGF; (Darriba et al., 2011)) on a trimmed alignment (trimAl; Capella-Gutierrez et al. 2009). α-catenins are colored blue, vinculins are colored green, amoebozoan sequences are colored yellow, and ungrouped sequences are colored grey. Corresponding schematics of domain architecture are grouped adjacent to appropriate clades.
(B) A general schematic of the domain architecture of α-catenin and vinculin, with a bar graph indicating the average percent amino acid sequence identity of the highlighted regions within each protein family.