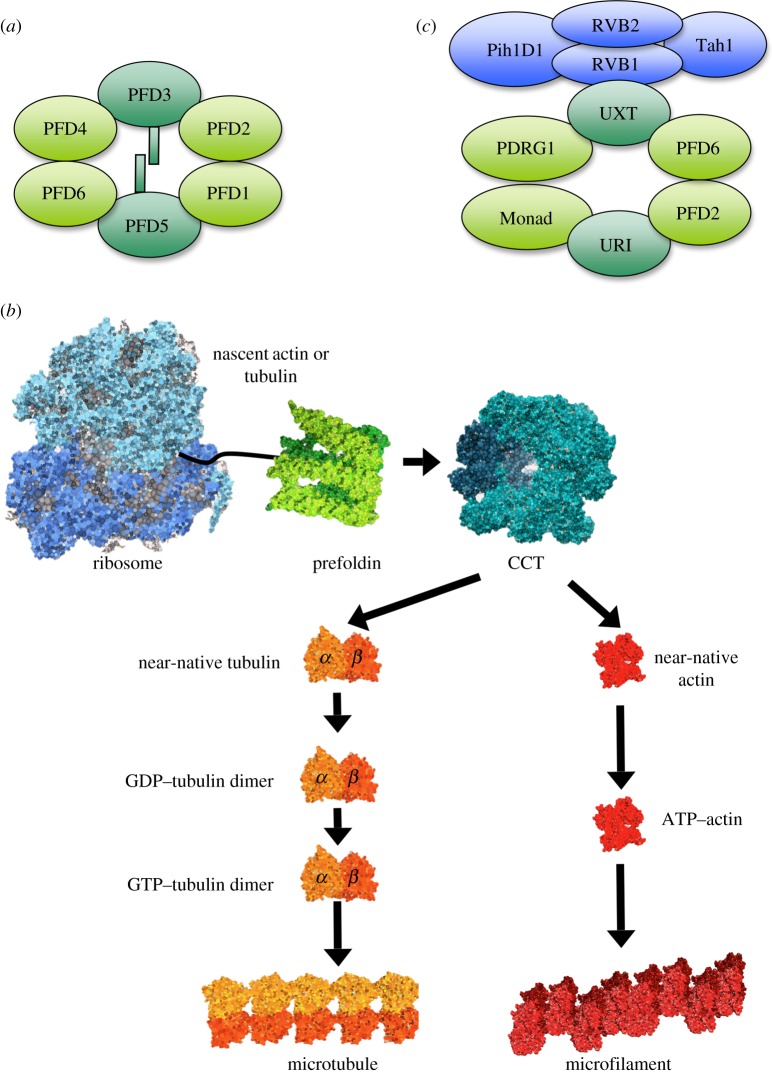
Figure 1.
The prefoldin complex. (a) Canonical prefoldin is a heterohexameric complex composed of two α subunits (dark green), which play a central structural role, and four β subunits (light green). (b) The best-characterized function of prefoldin is the cotranslational folding of proteins. Prefoldin binds unfolded polypeptides and transfers them to the ATP-dependent chaperon CCT prior to its assembly into high-order protein structures, such as microtubules and actin filaments. (c) In addition to canonical complexes, which retain the structure of archaeal prefoldin, eukaryotes exhibit prefoldin-like complexes. In these, the two α and some of the β canonical subunits are replaced with alternative polypeptides. Prefoldin-like complexes interact and functionally cooperate with other cochaperones such as the R2TP complex (purple).